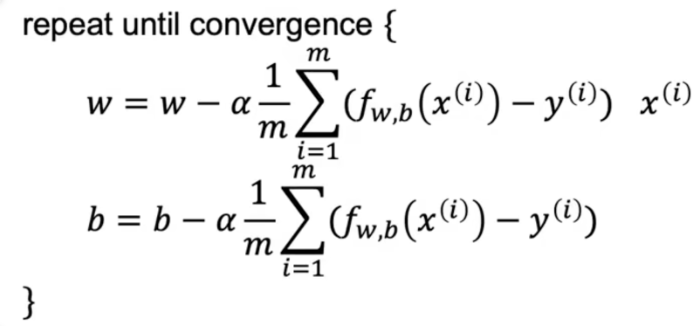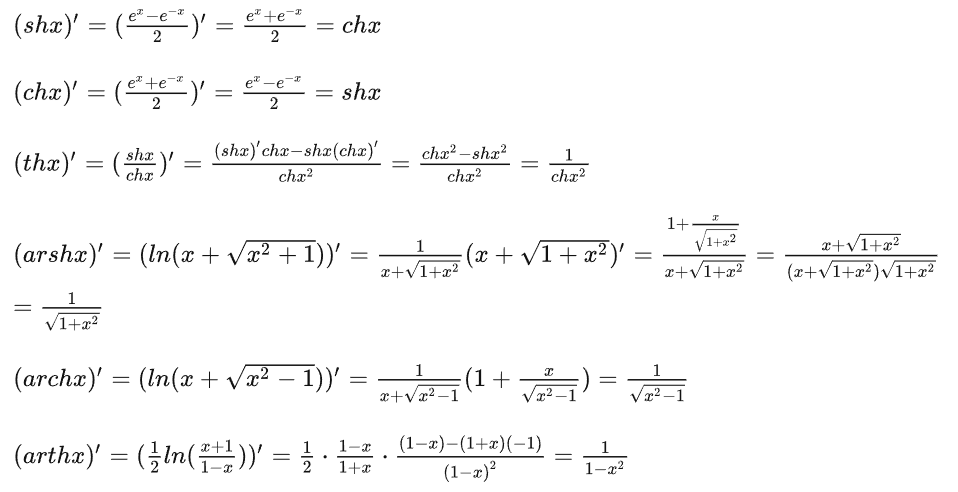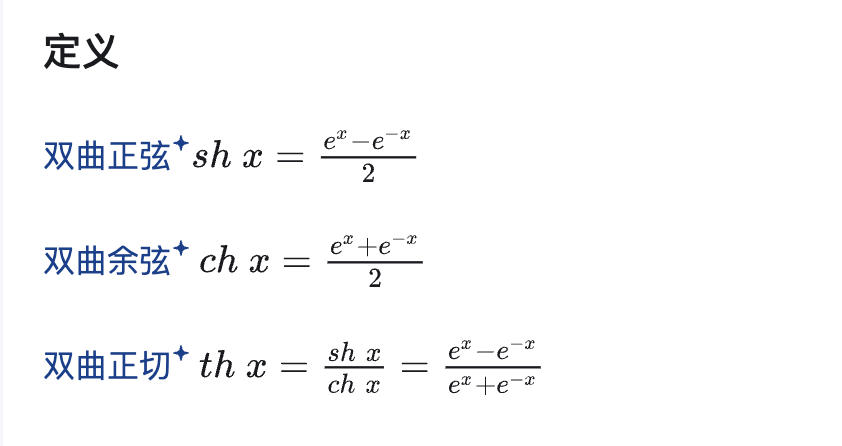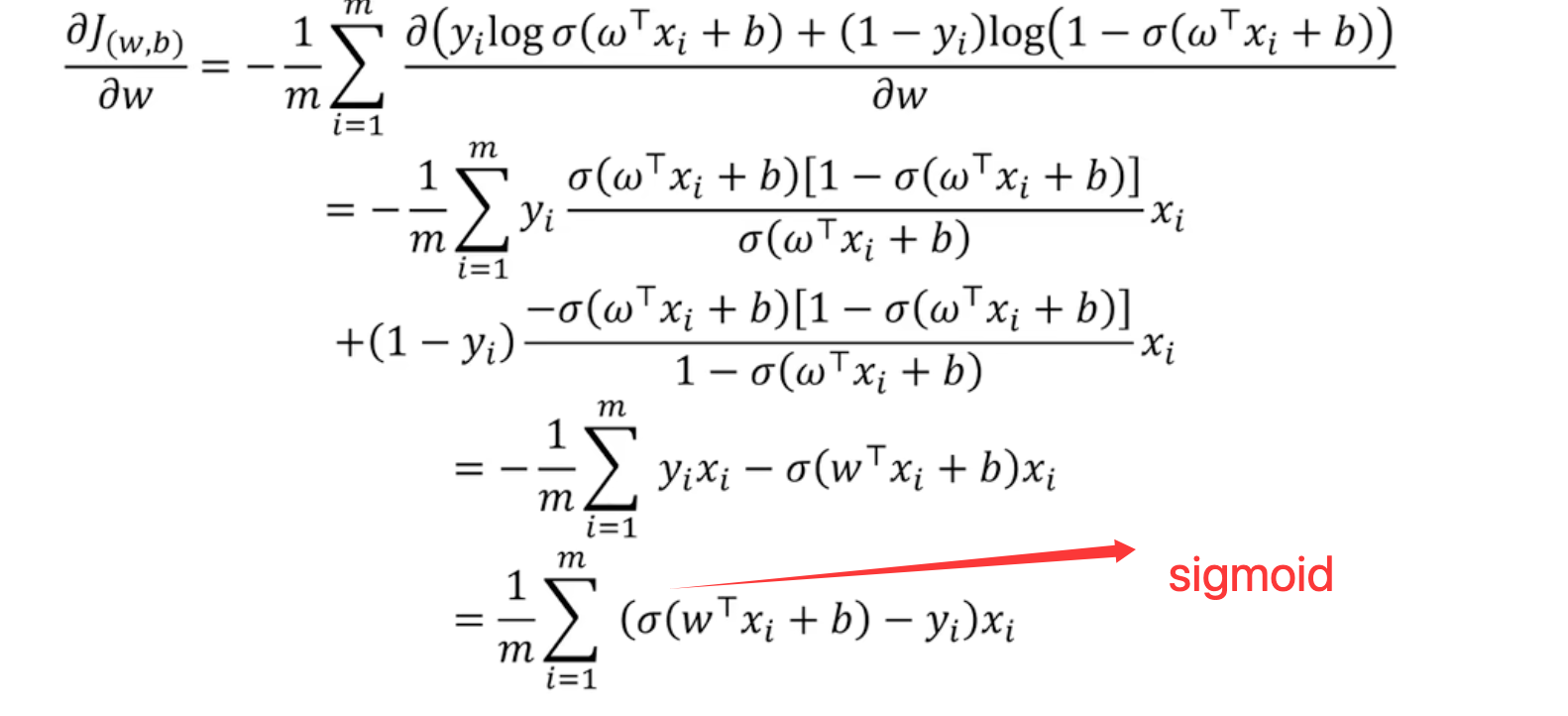教程地址:
up **:炮哥带你学
课程名字:[手把手教学]快速带你入门深度学习与实战
简介:入门机器学习和深度学习
网址:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1eP411w7Re/?spm_id_from=333.1387.homepage.video_card.click&vd_source=f8d1f5518d3f58b48b5c428323f8d3bf
up **:炮哥带你学
课程名字:Pytorch框架与经典卷积神经网络与实战
简介:入门深度学习和pytorch
网址:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1e34y1M7wR/?spm_id_from=333.1387.homepage.video_card.click&vd_source=f8d1f5518d3f58b48b5c428323f8d3bf
简介
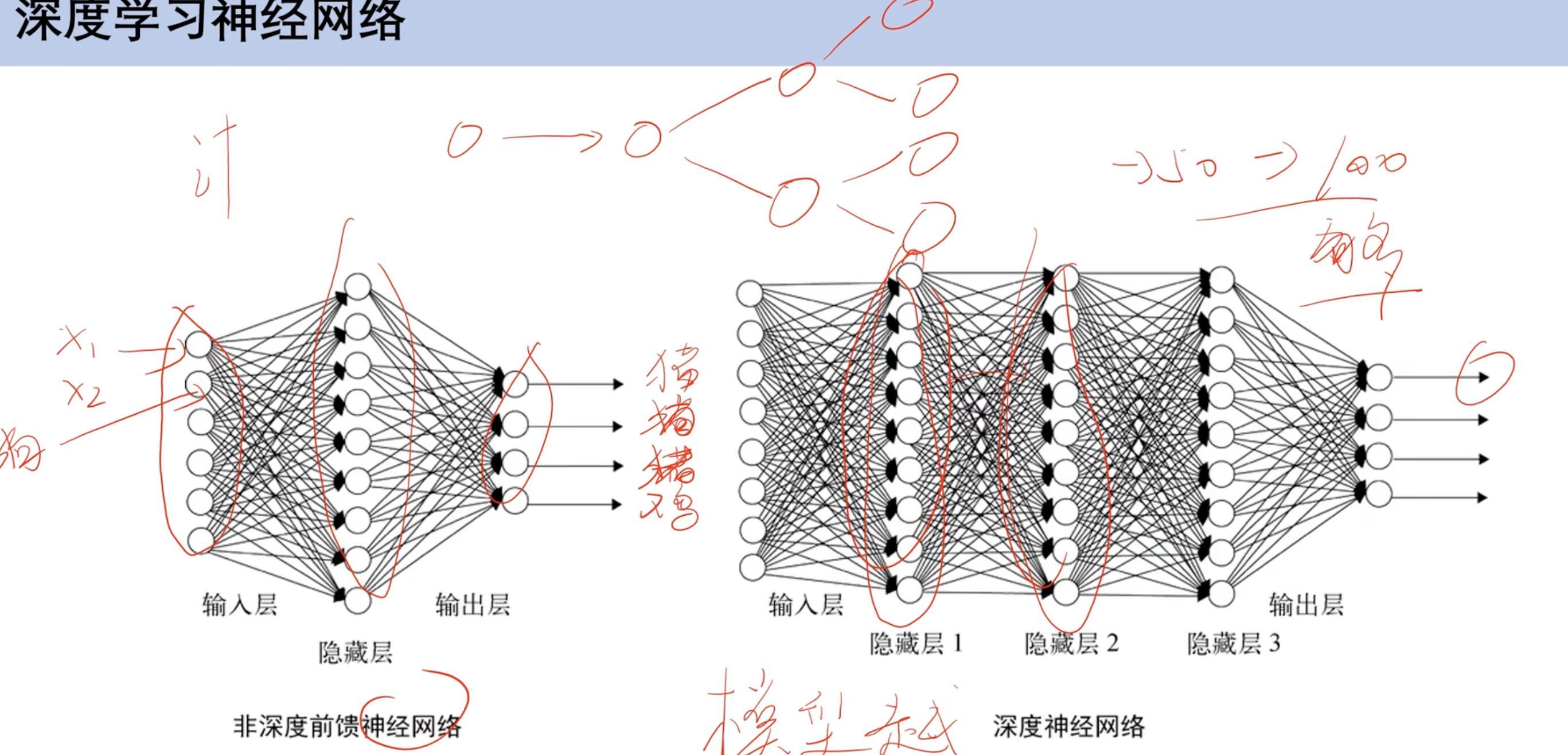
深度学习以神经网络为基础
神经网络
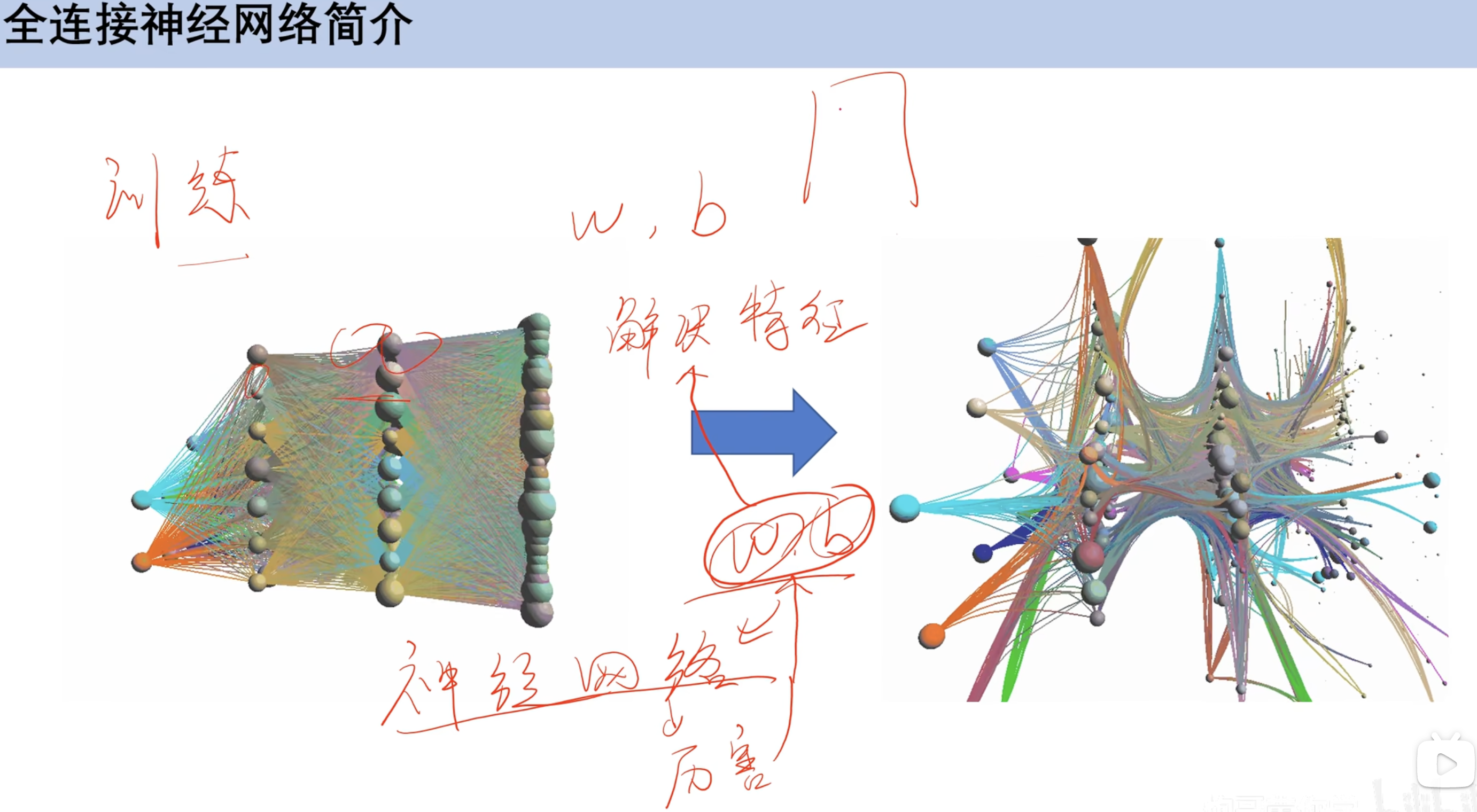
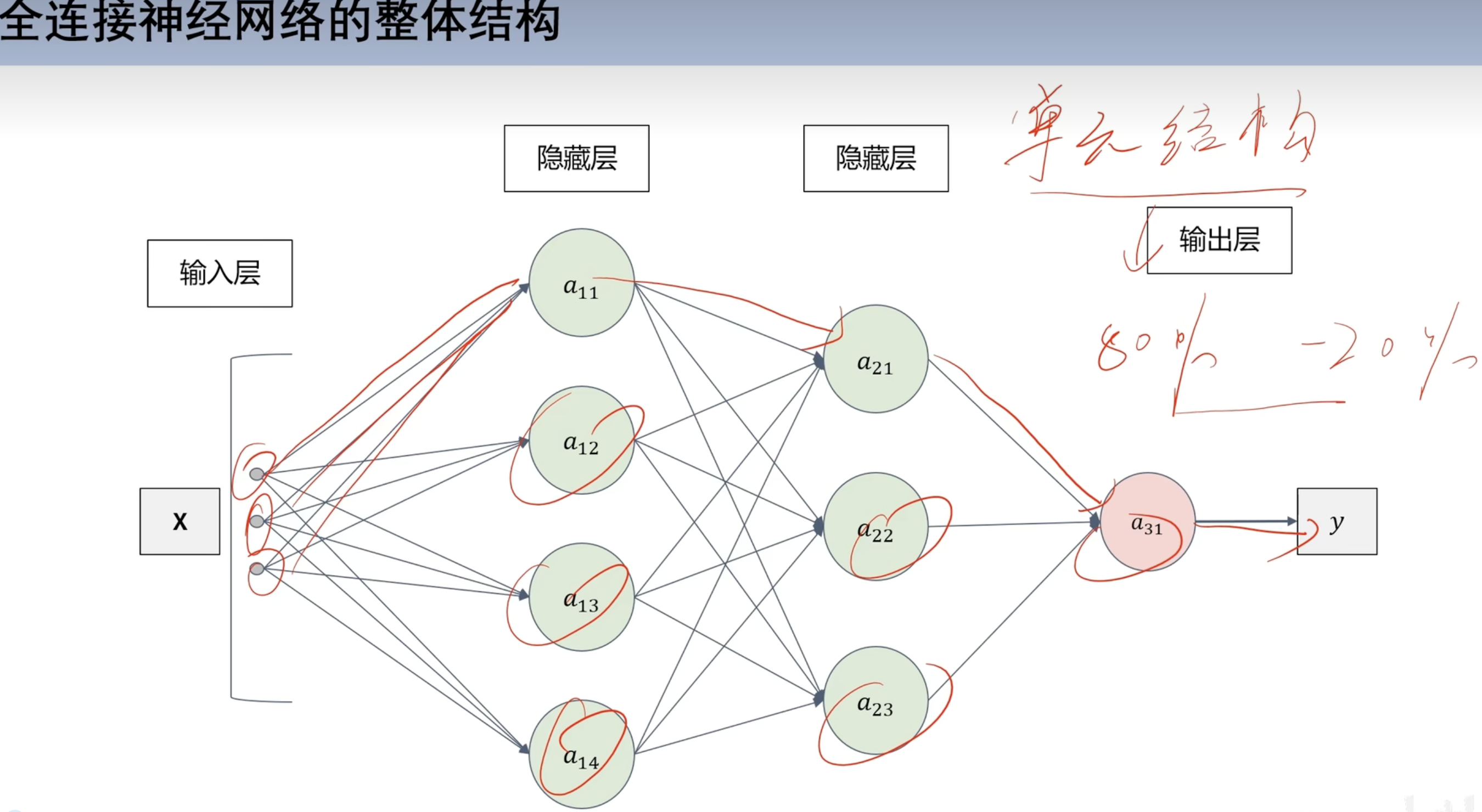
全连接神经网络
通过训练w和b(权重和偏置)
神经网络作用 ==深度学习框架介绍== 环境介绍 机器学习知识回顾 2. 线性回归模型与梯度下降 2.2 定义
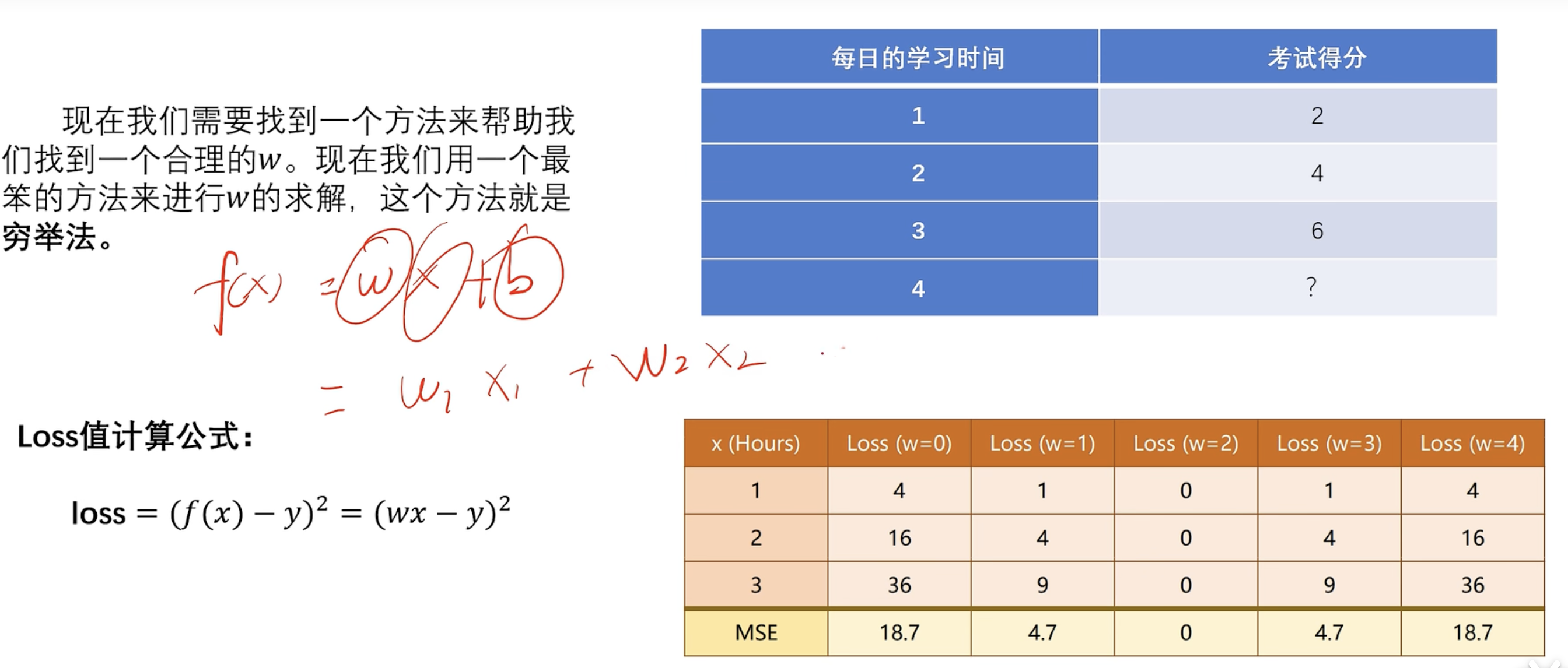
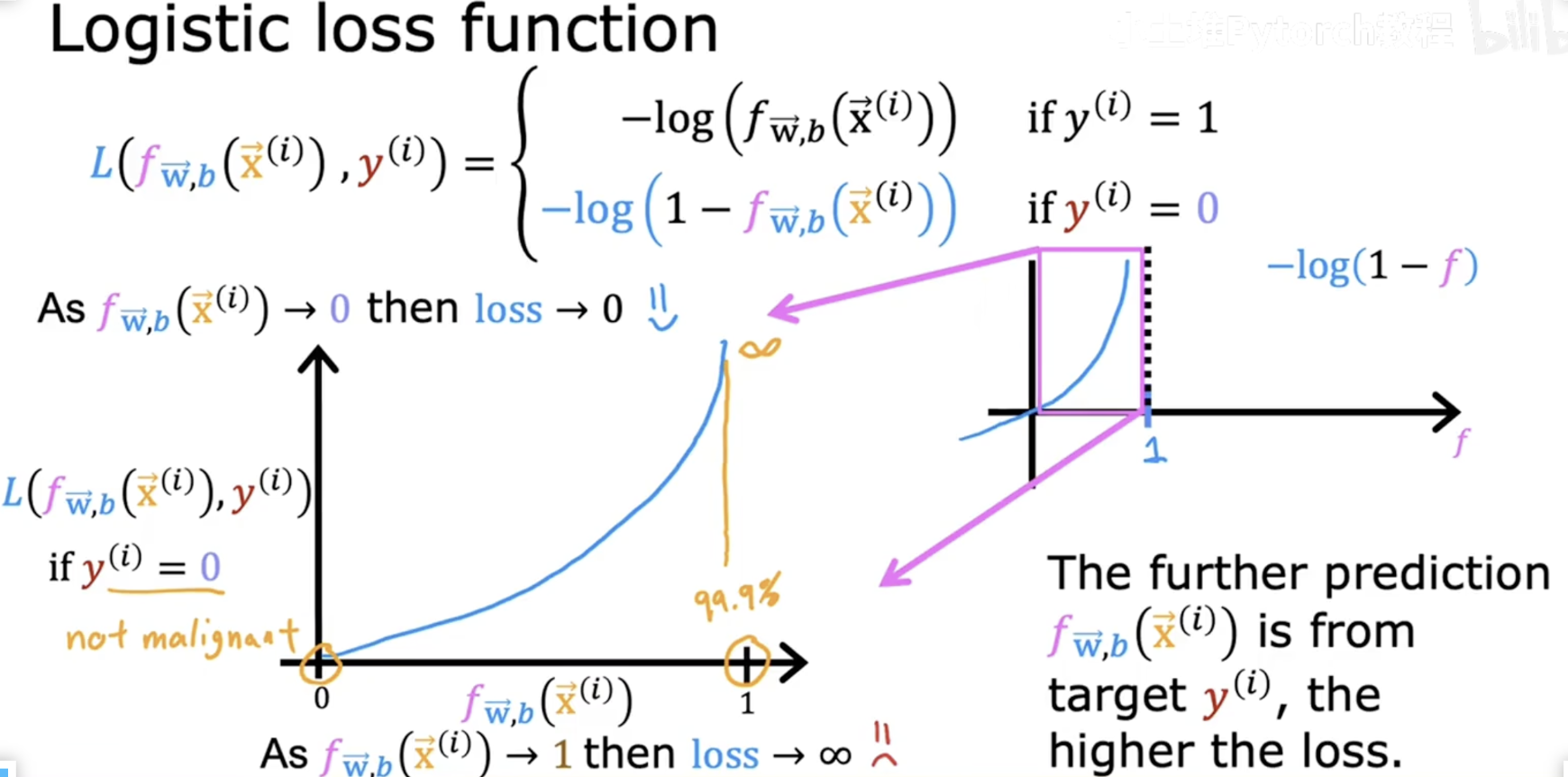
损失函数 (误差函数) 穷举法
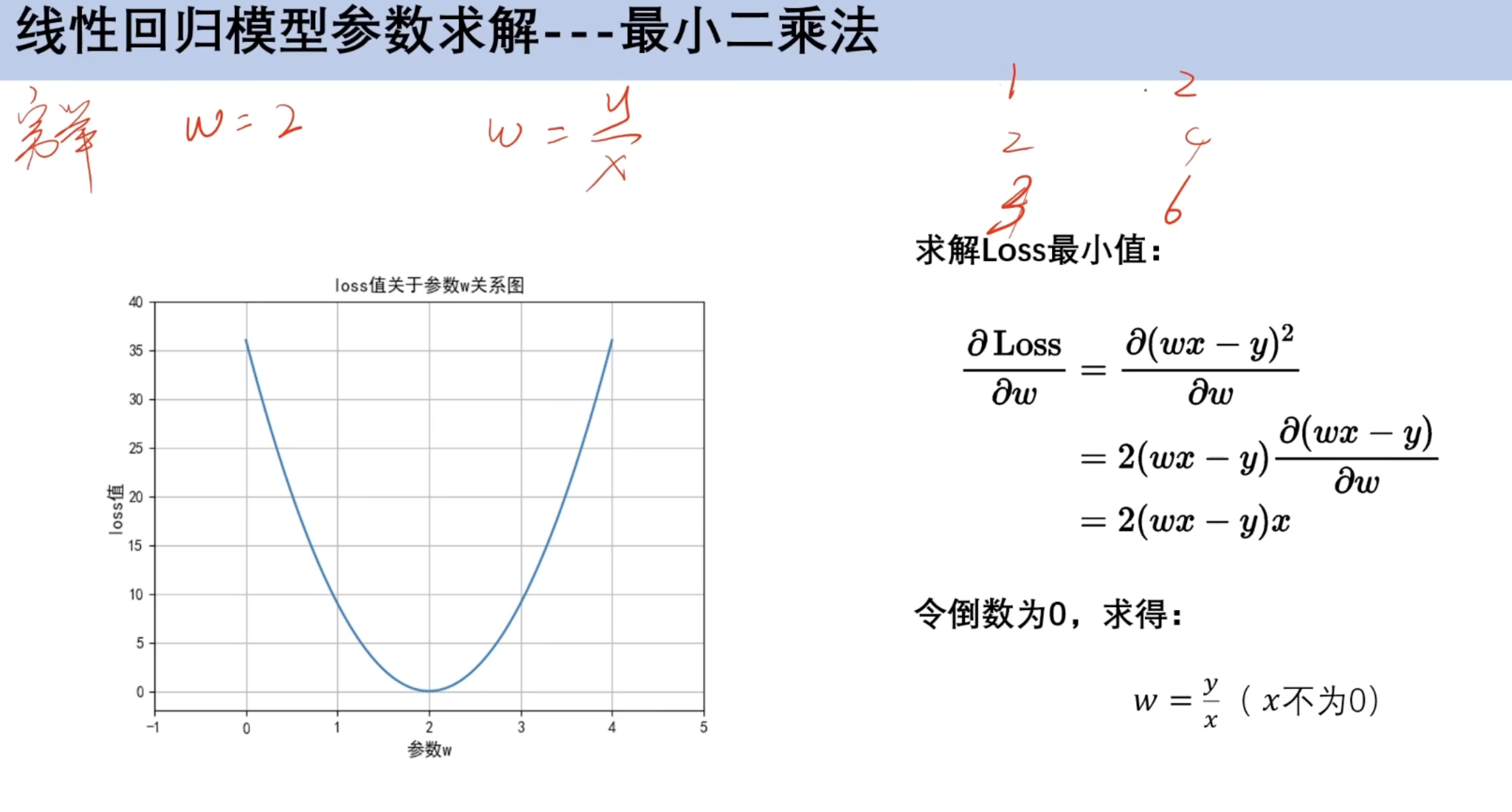
2.3 最小二乘法
对x求偏导
向量版本
对损失函数求导
并非所有矩阵有可逆矩阵,因此引入损失函数
==2.3 梯度下降== 理解 公式 $$
简化版本
$$
案例 实战案例
步骤:
数据
模型
损失函数
梯度求导
利用梯度更新参数
设置训练轮次
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 x_data = [1 , 2 , 3 ] y_data = [2 , 4 , 6 ] w = 4 def forword (x ): return x * w def cost (xs, ys ): costvalue = 0 for x, y in zip (xs, ys): y_pred = forword(x) costvalue += (y_pred - y) ** 2 return costvalue / len (xs) def gradient (xs, ys ): grad = 0 for x, y in zip (xs, ys): grad += 2 * x * (forword(x) - y) return grad / len (xs) aa = 0.01 for epoch in range (100 ): cost_val = cost(x_data, y_data) gra_val = gradient(x_data, y_data) w = w - aa * gra_val print ('训练轮次:' , epoch, 'w=' , w, 'loss:' , cost_val) print ('100轮后w已经训练好了' , 'w=' , w)print ("学习4小时最终得分为:" , forword(4 ))
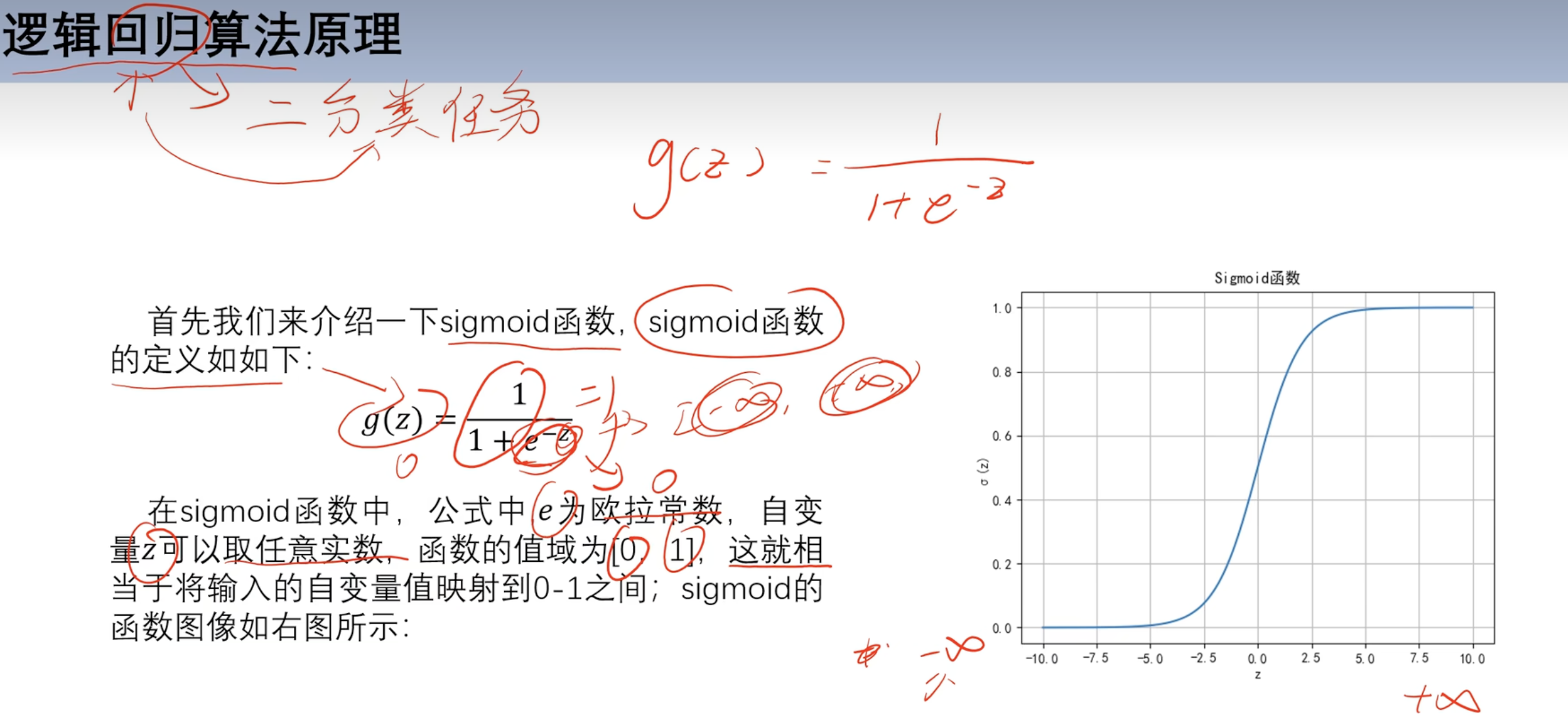
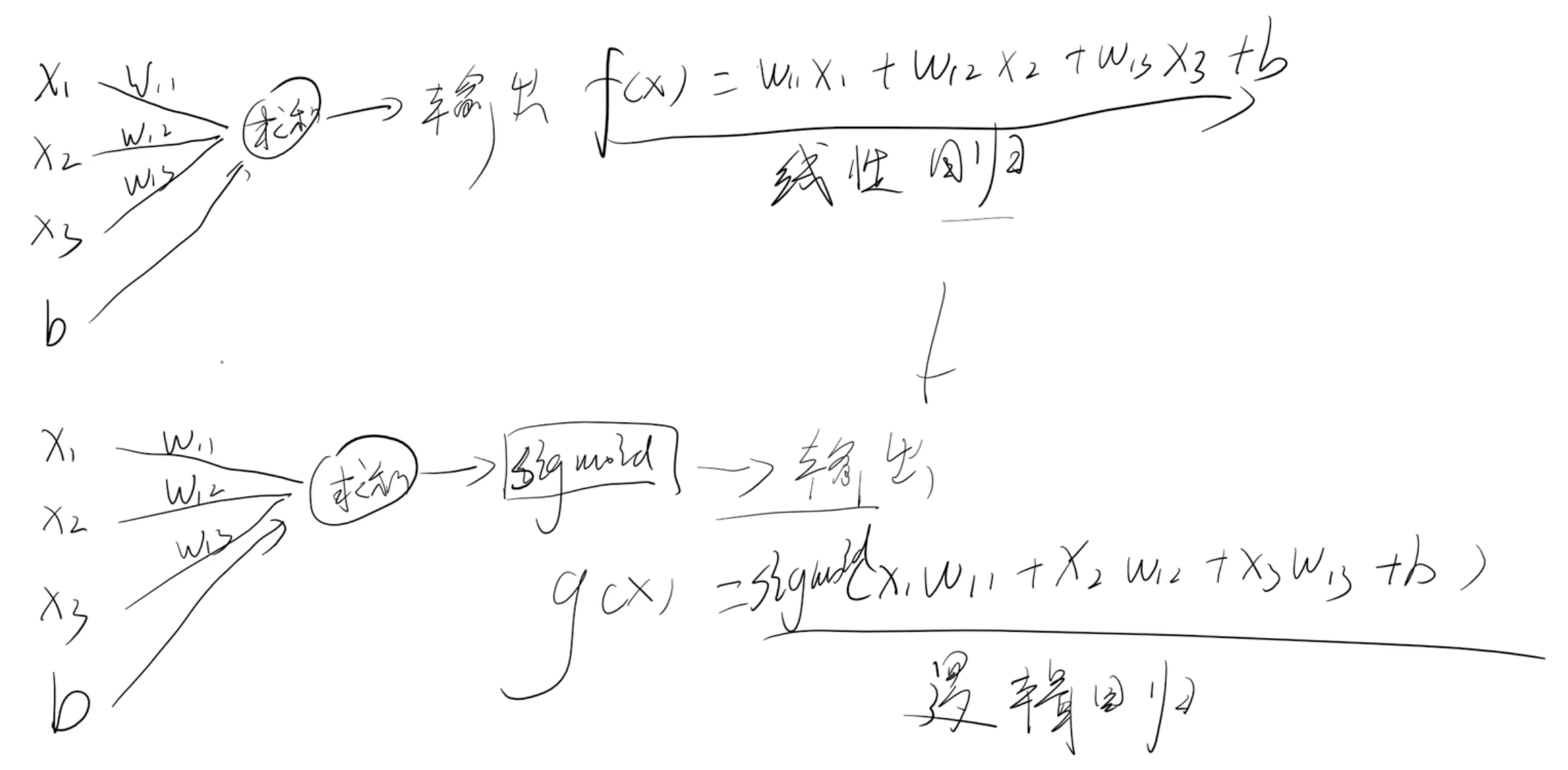
==3.逻辑回归== 3.1 回归和分类的区别 3.2 sigmoid函数 求导
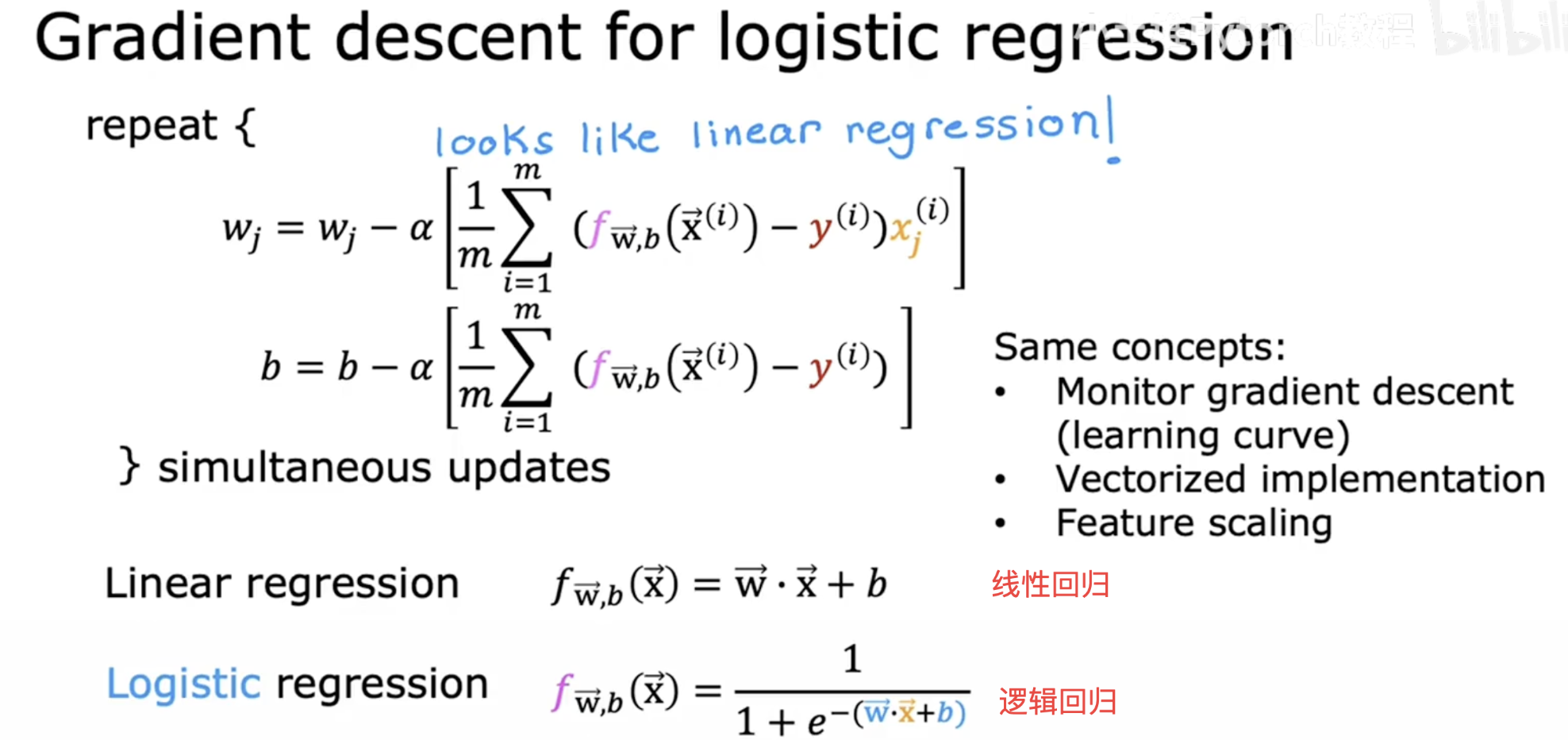
==3.3 损失函数== 表达式 ==3.4 梯度下降== 参数w更新
向量求导
参数b更新 3.5 回归模型评价指标 案例 准确率 精确率 召回率
F1值
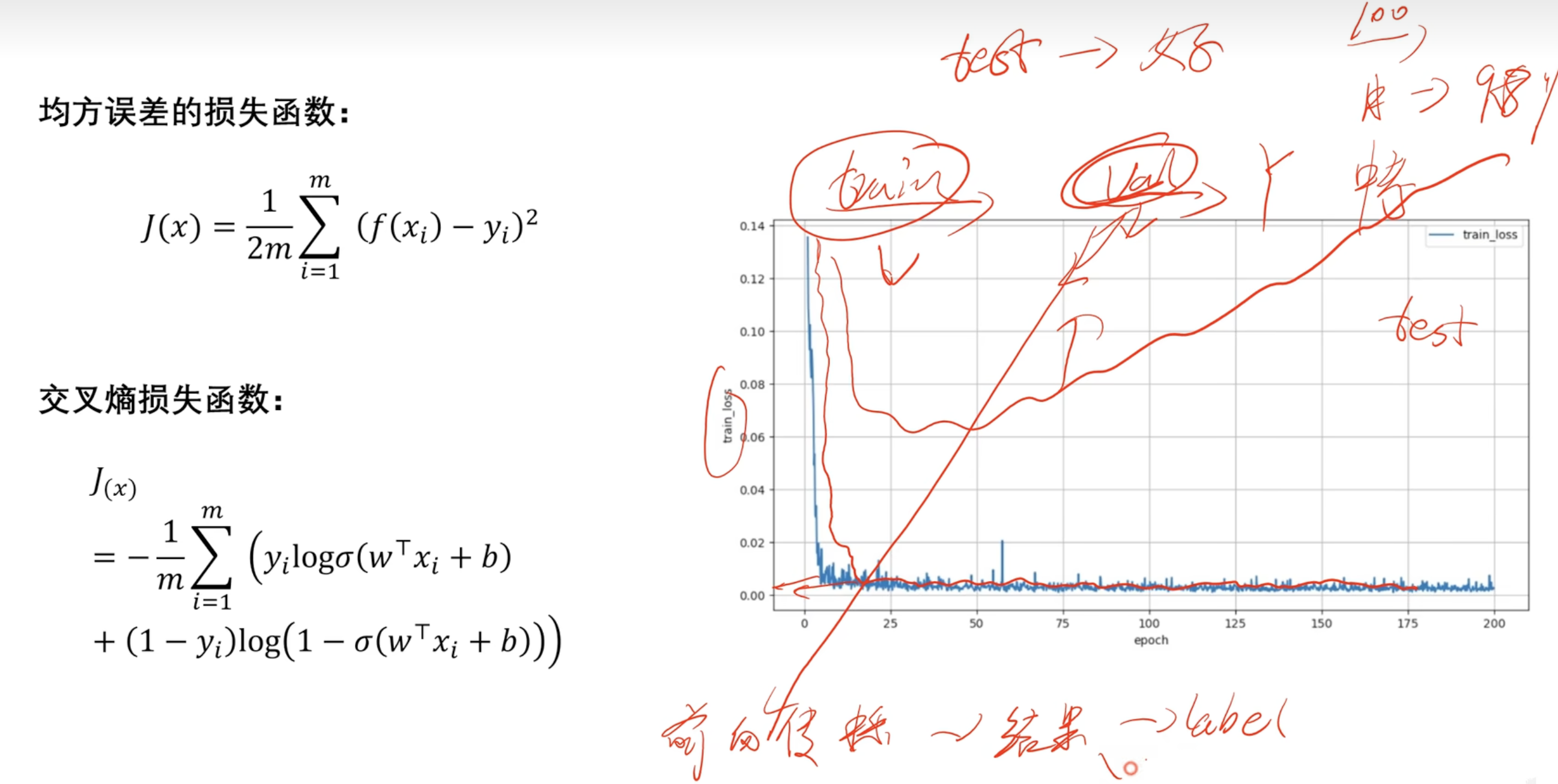
3.6 分类模型评价指标 平均绝对误差(MAE)和==均方误差(MSE)==
MSE 就是前面的LOSS 损失函数
均方根误差(RMSE) 平均绝对百分比误差(MAPE) 3.7 实战案例 代码
归一化公式:(X-min)/(max-min),消除量纲和数值大小对结果的影响
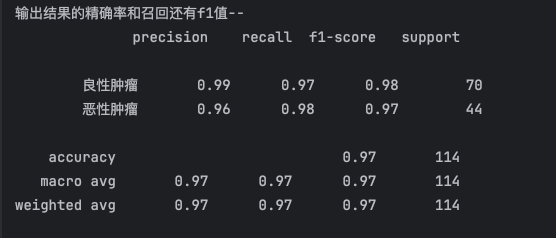
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport pandas as pdfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_reportdataset = pd.read_csv("breast_cancer_data.csv" ) X = dataset.iloc[:, :-1 ] Y = dataset['target' ] x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2 ) sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0 , 1 )) x_train = sc.fit_transform(x_train) x_test = sc.transform(x_test) lr = LogisticRegression() lr.fit(x_train, y_train) print ("w" , lr.coef_)print ("b" , lr.intercept_)pre_result = lr.predict(x_test) print ("预测结果:" , pre_result)pre_result_proba = lr.predict_proba(x_test) print ("概率:" , pre_result_proba)pre_list = pre_result_proba[:, 1 ] print (pre_list)result = [] result_name = [] thresholds = 0.3 for i in range (len (pre_list)): if pre_list[i] > thresholds: result.append(1 ) result_name.append("恶性" ) else : result.append(0 ) result_name.append("良性" ) print ("打印阈值调整后结果:" )print (result)print (result_name)print (y_test)report = classification_report(y_test, result, labels=[0 , 1 ], target_names=['良性肿瘤' , '恶性肿瘤' ]) print ("输出结果的精确率和召回还有f1值--" )print (report)
结果打印
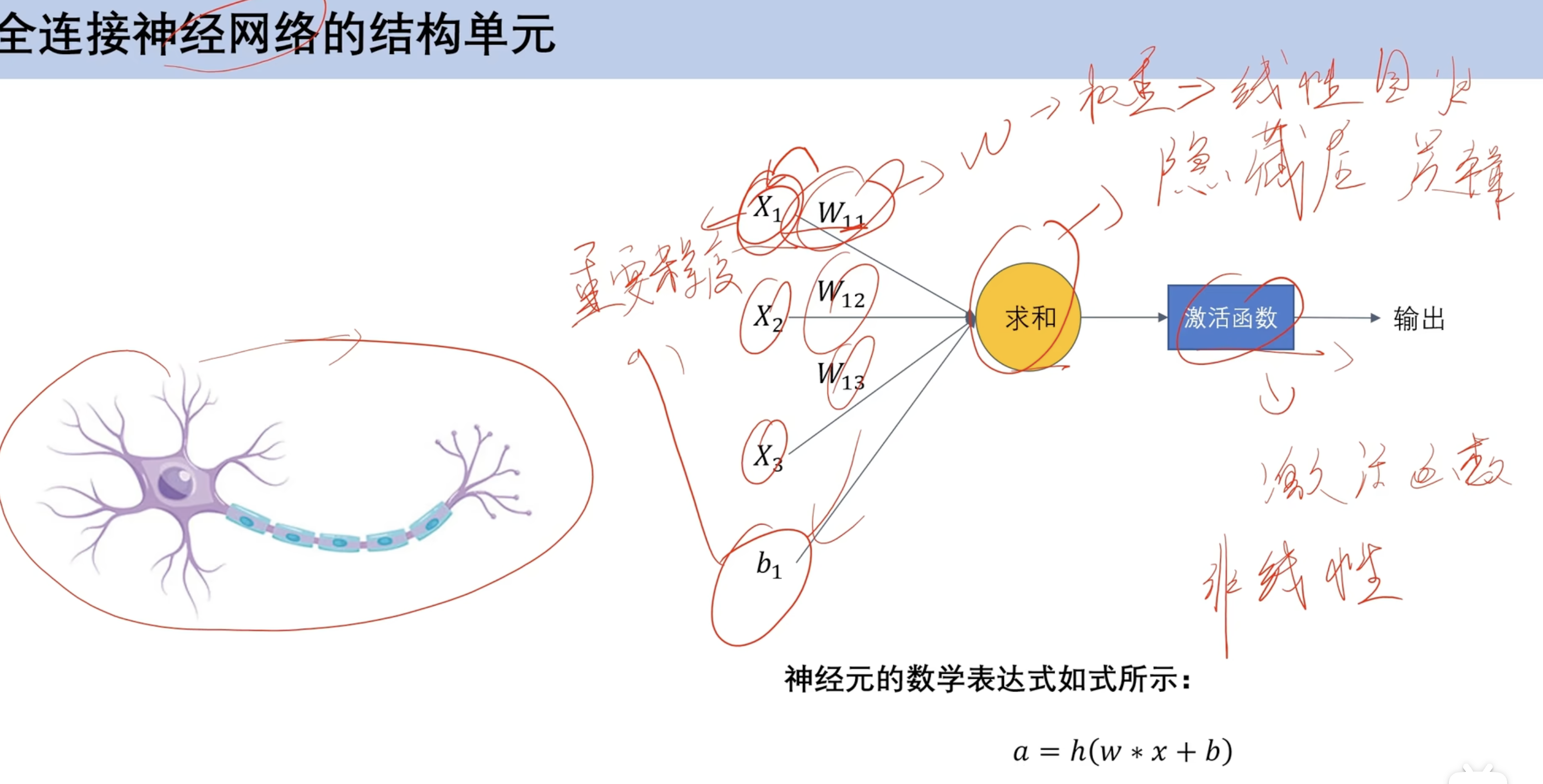
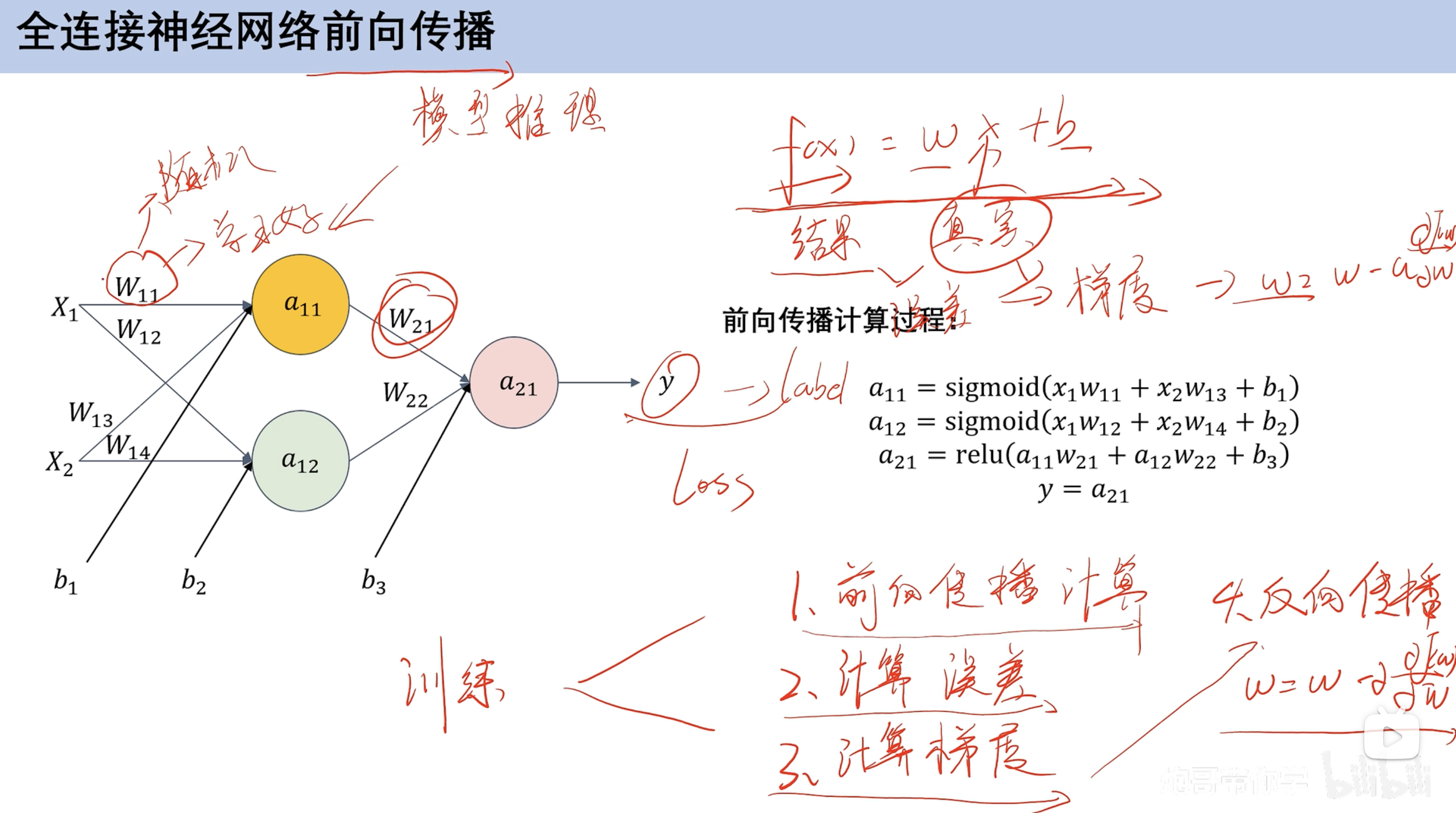
深度学习 全连接神经网络 结构 结构单元
x 输入
b 偏置
w权重
求和:隐藏层
激活函数:非线性 ==(对比逻辑回归激活函数是求和 逻辑回归激活函数是sigmoid)==
对比机器学习激活函数
对比逻辑回归激活函数是求和 逻辑回归激活函数是sigmoid)
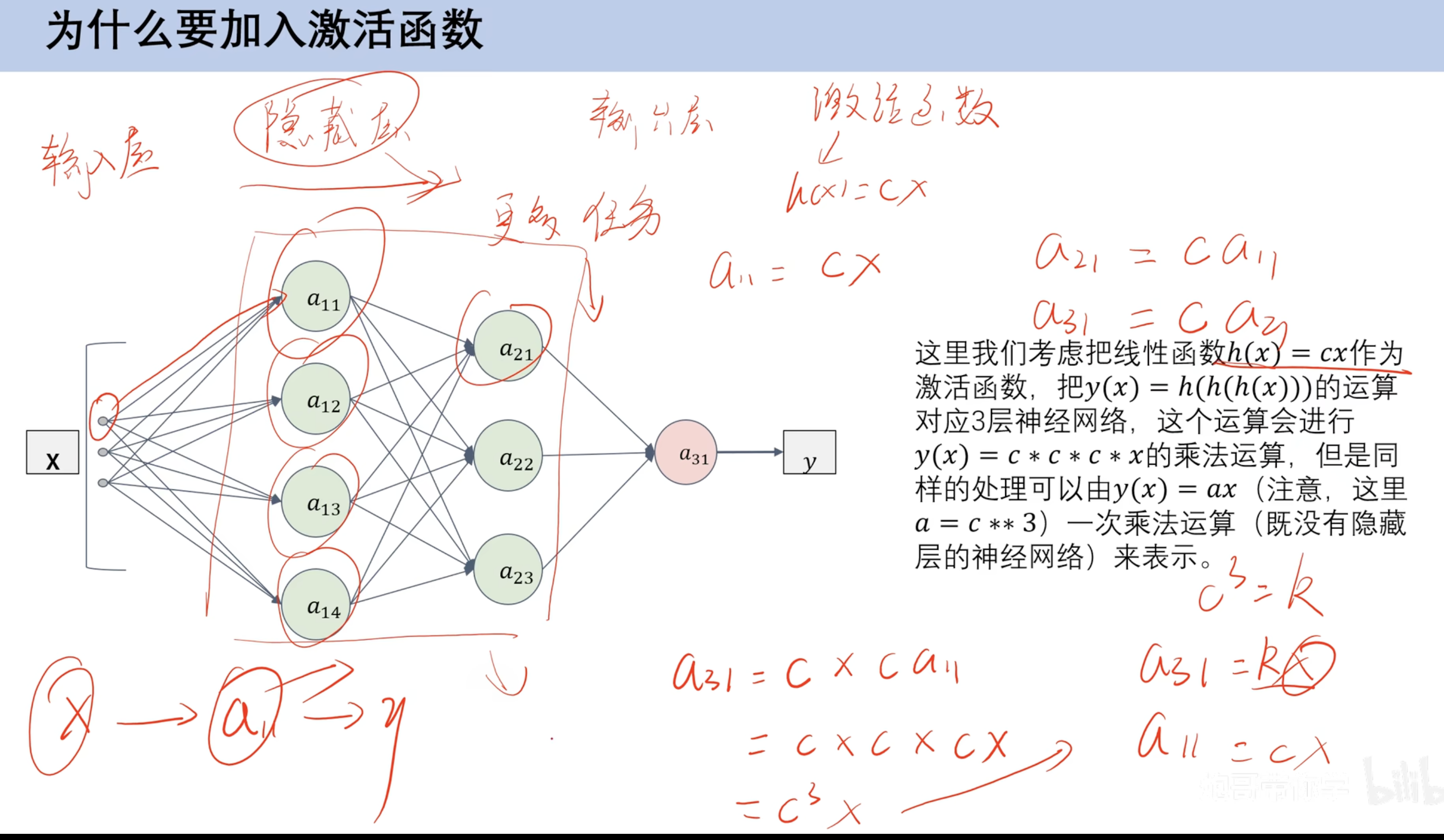
激活函数作用
激活函数
CSDN: 激活函数图像大全
https://blog.csdn.net/hy592070616/article/details/120617490
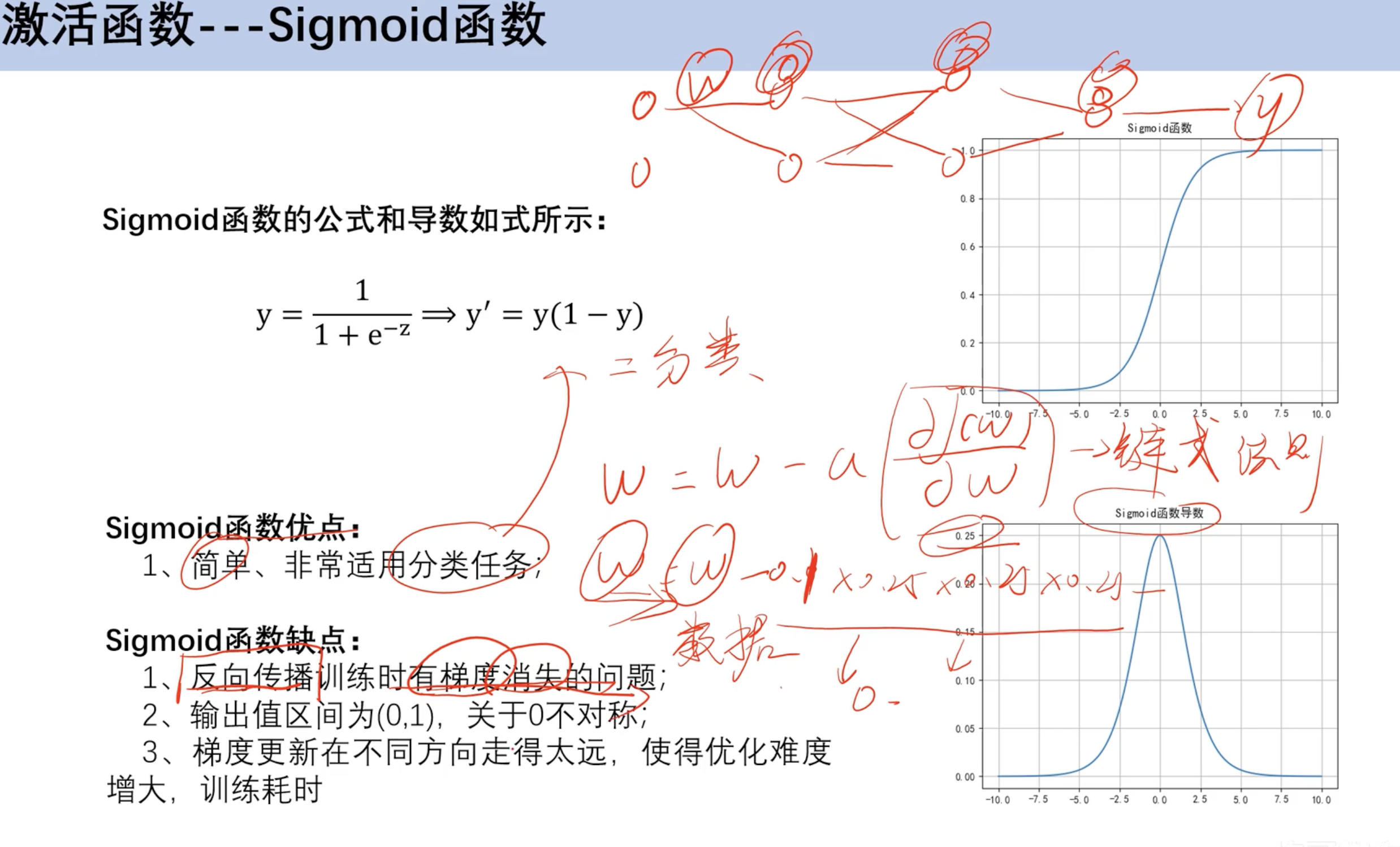
sigmoid函数
梯度消失问题,倒数图像左右消失太快 w累计乘法后小数累成 趋近于0
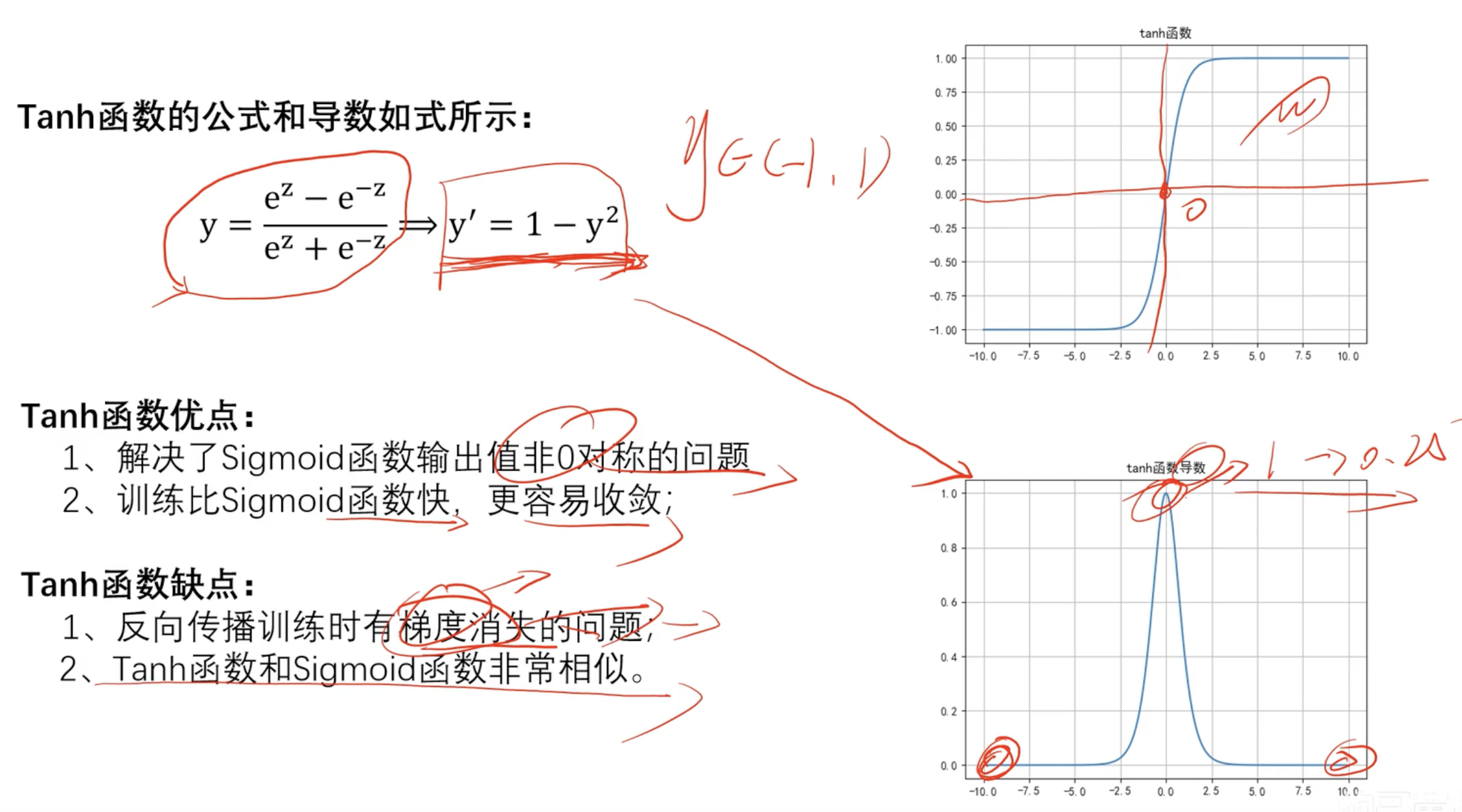
Tanh函数(双曲正切函数) 数学知识
知乎:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/563840693
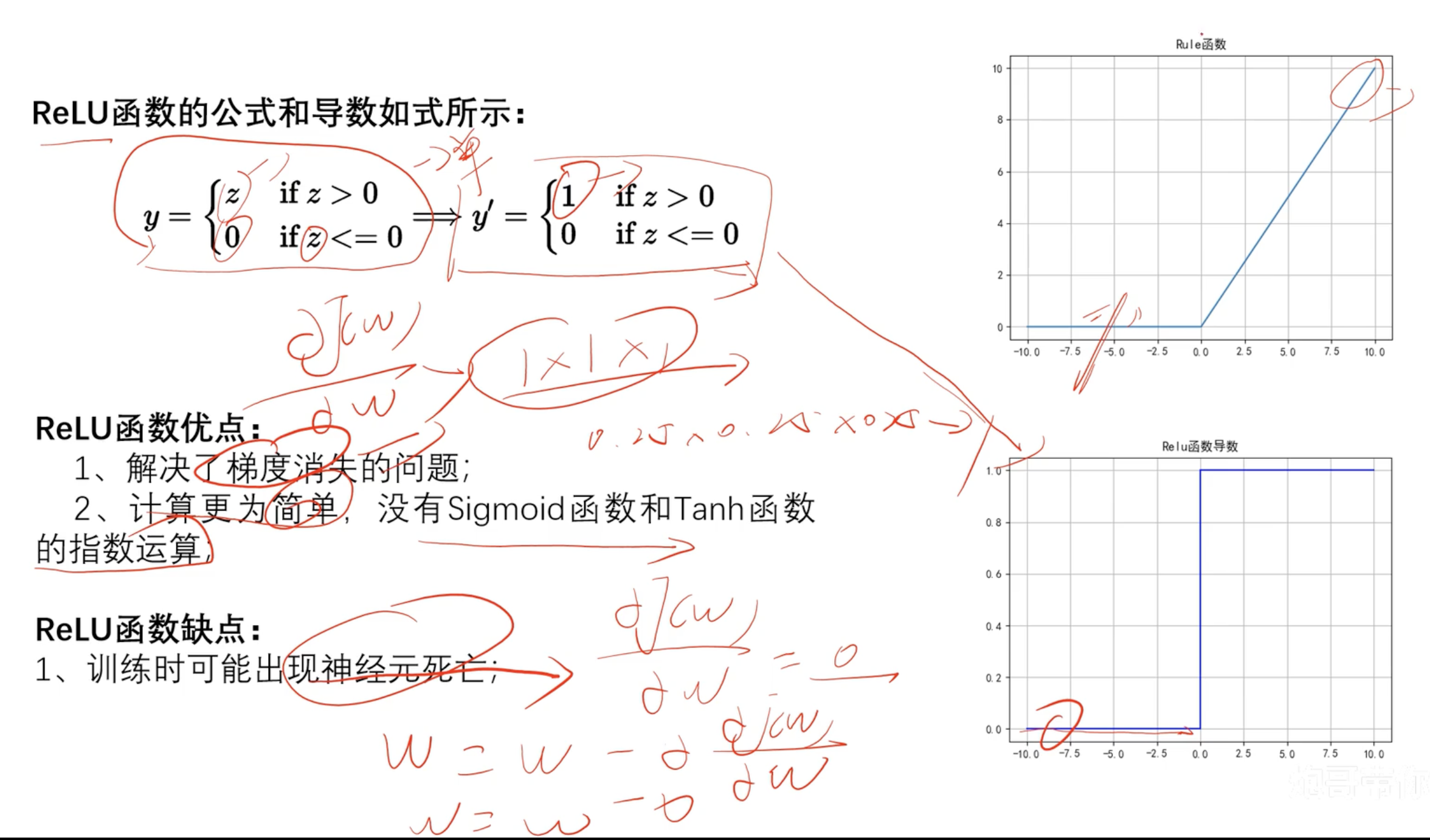
ReLU函数
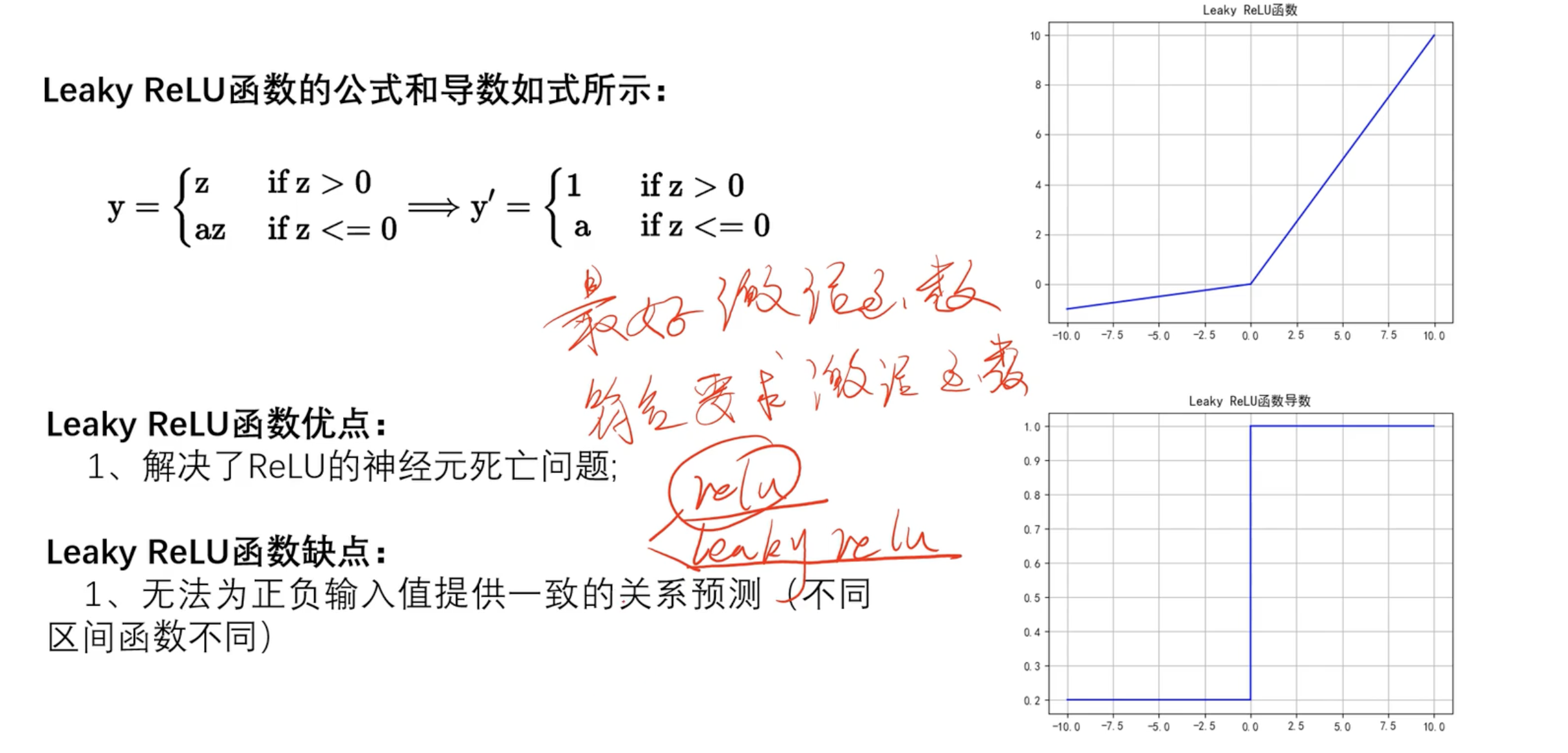
Leaky ReLU
SoftMax
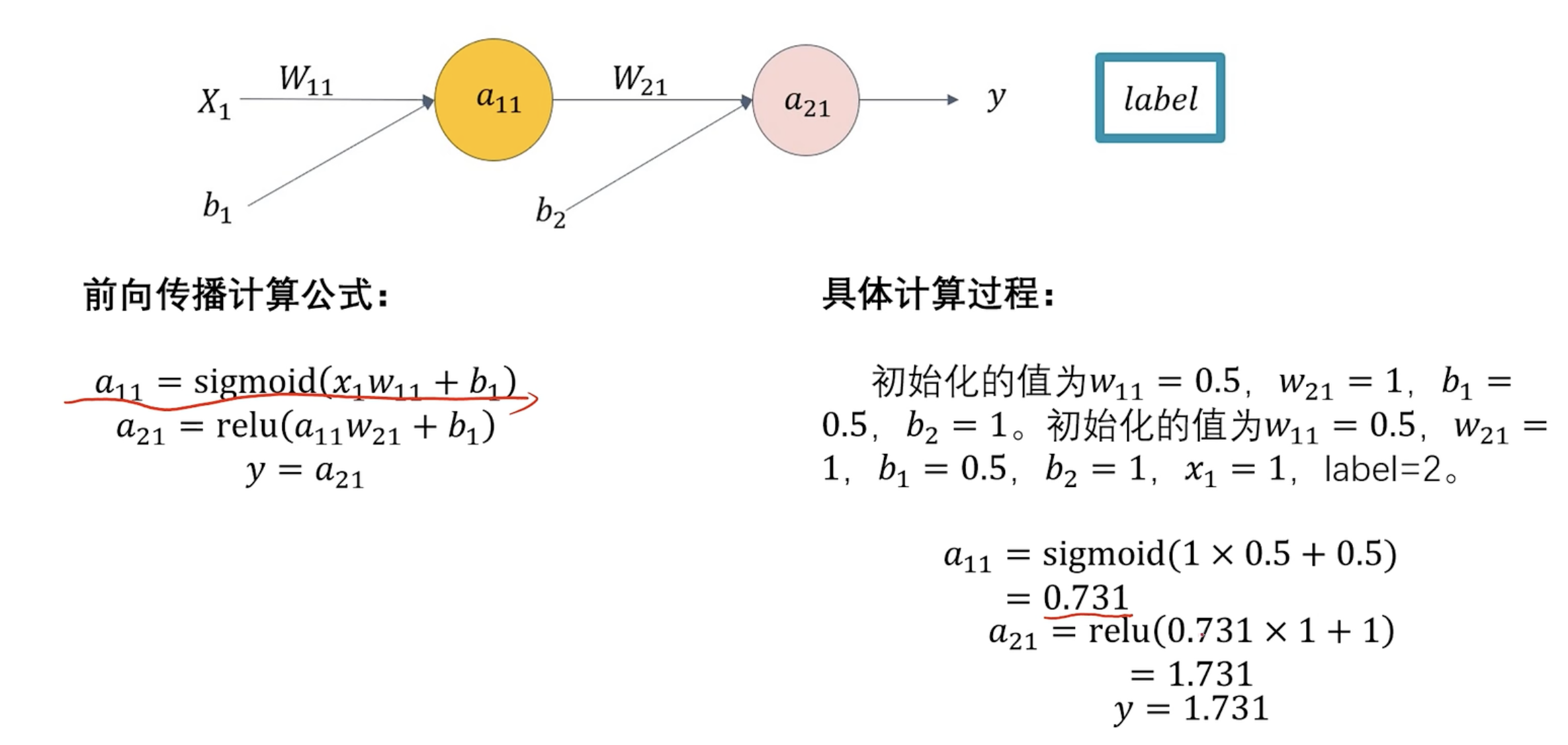
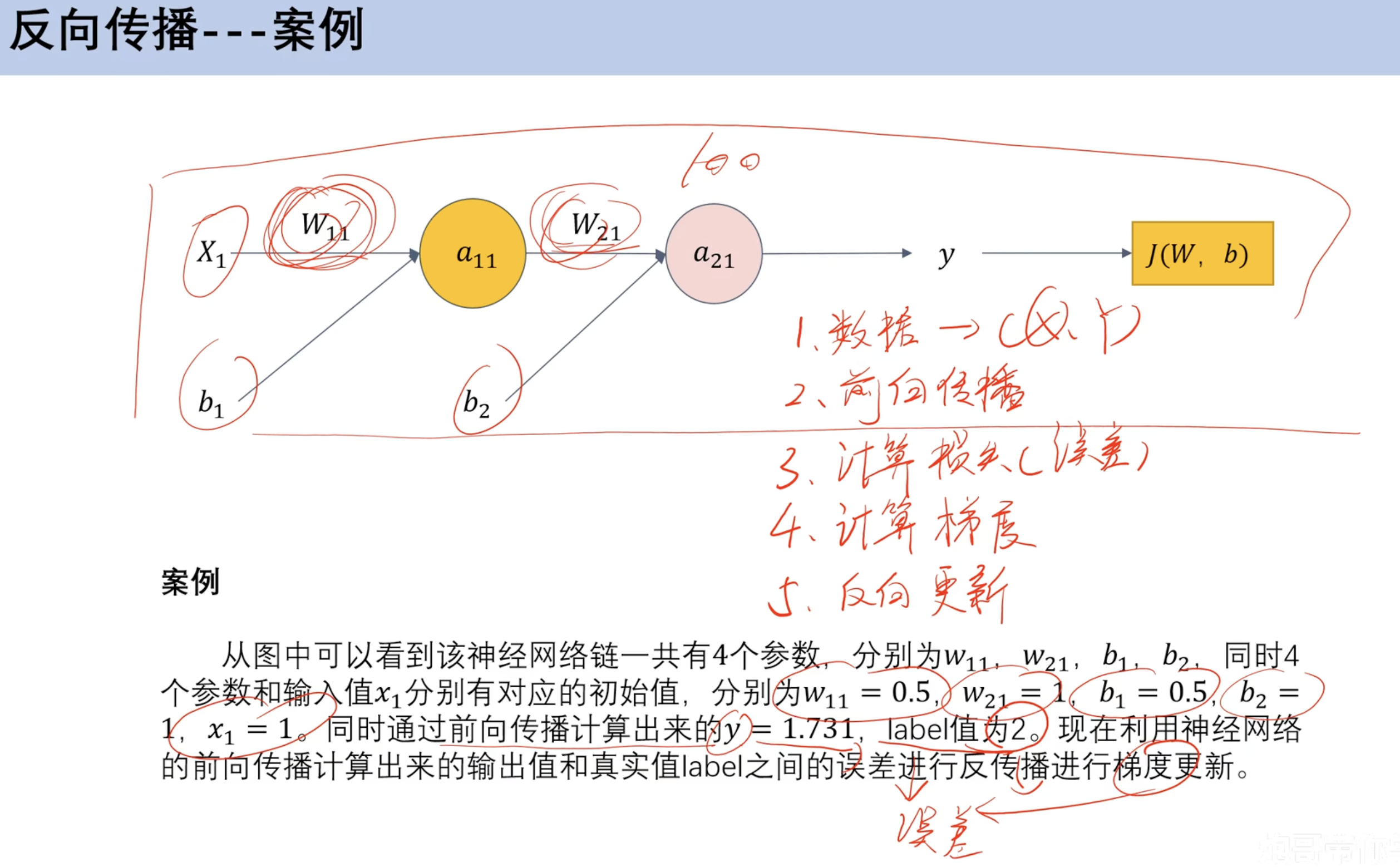
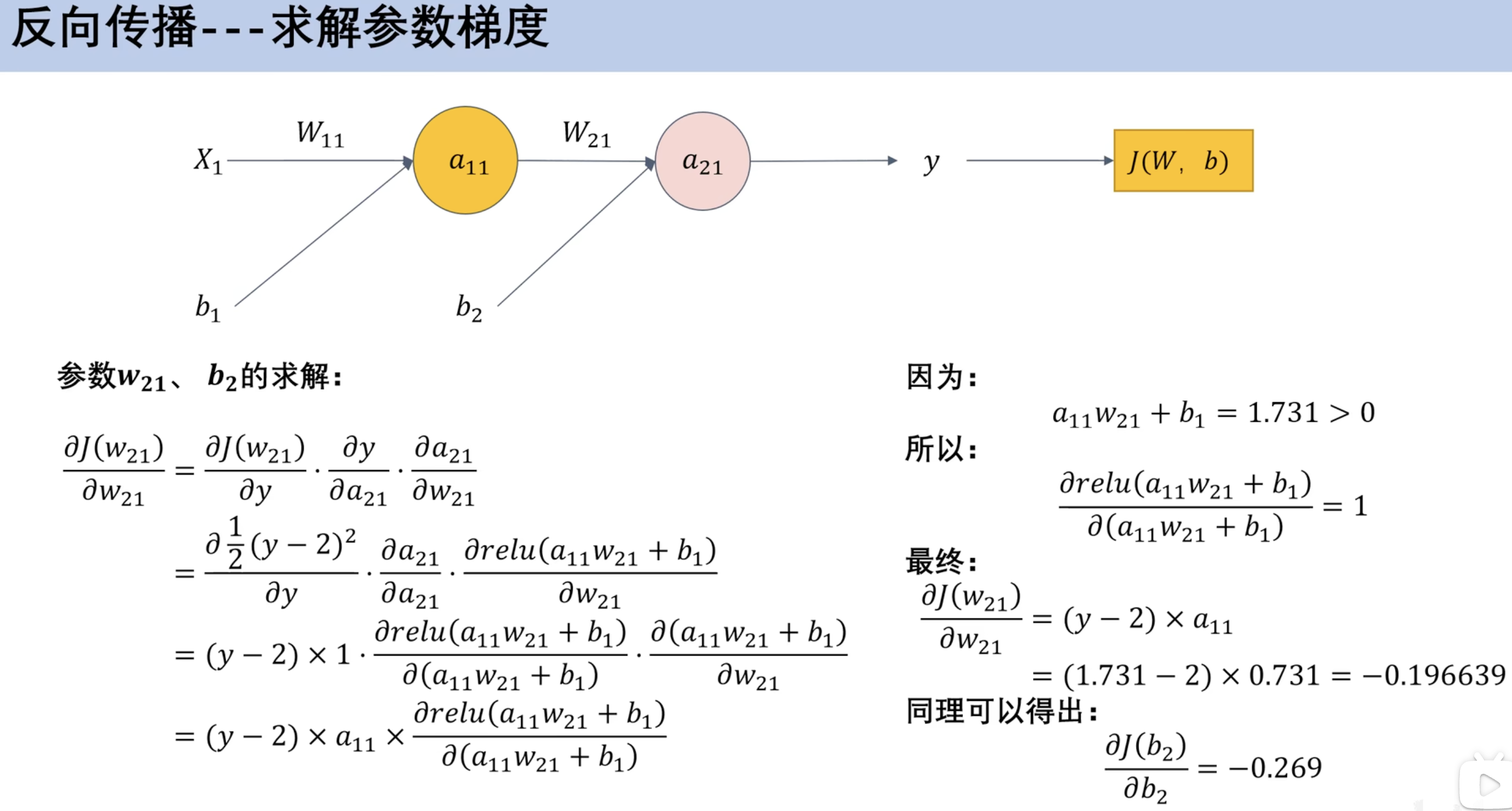
前向传播
前向传播计算 预设w和b 根据数据集计算计算误差 类比损失函数计算梯度 梯度更新 求损失函数偏导反向传播 反向更新w和b
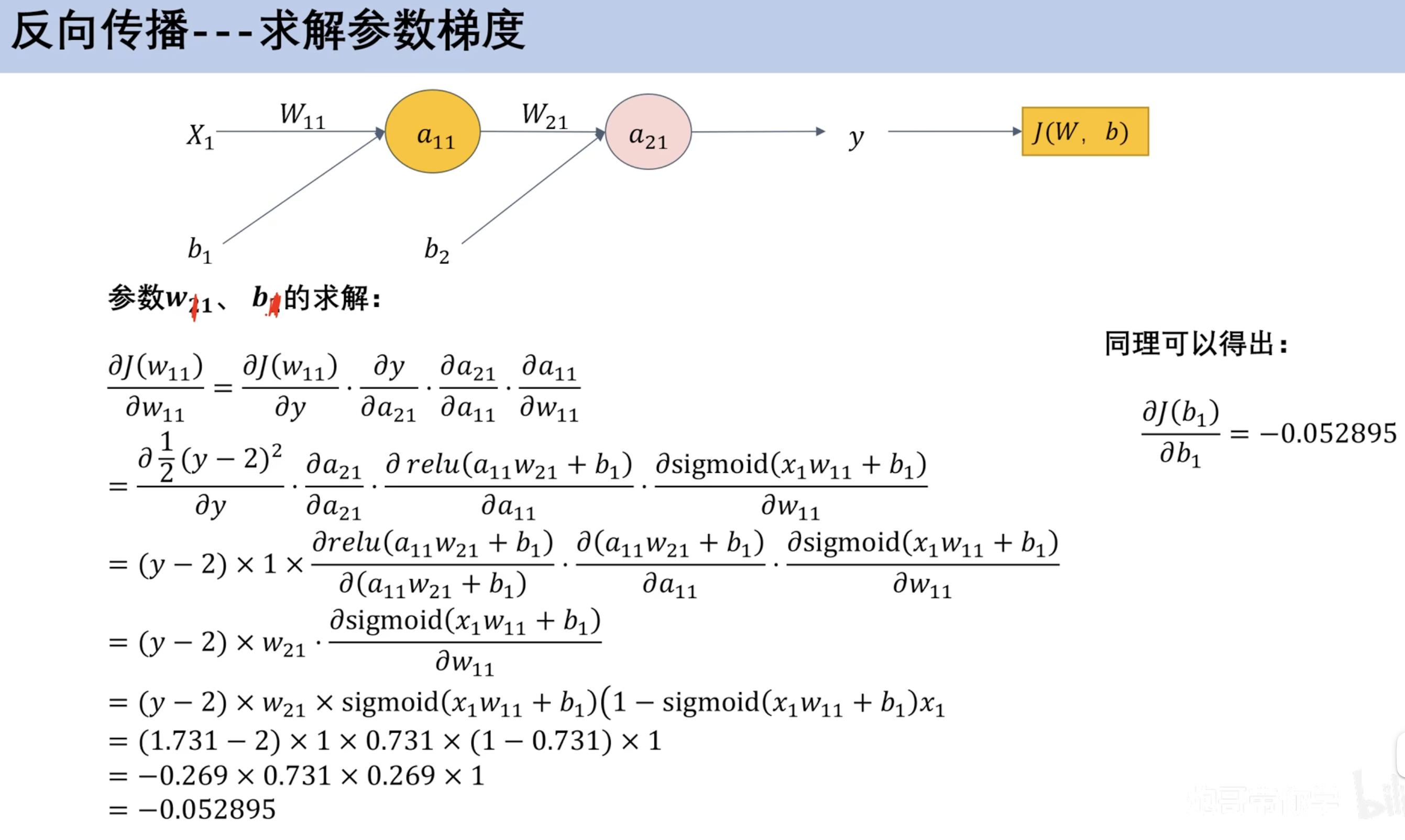
具体过程 损失函数
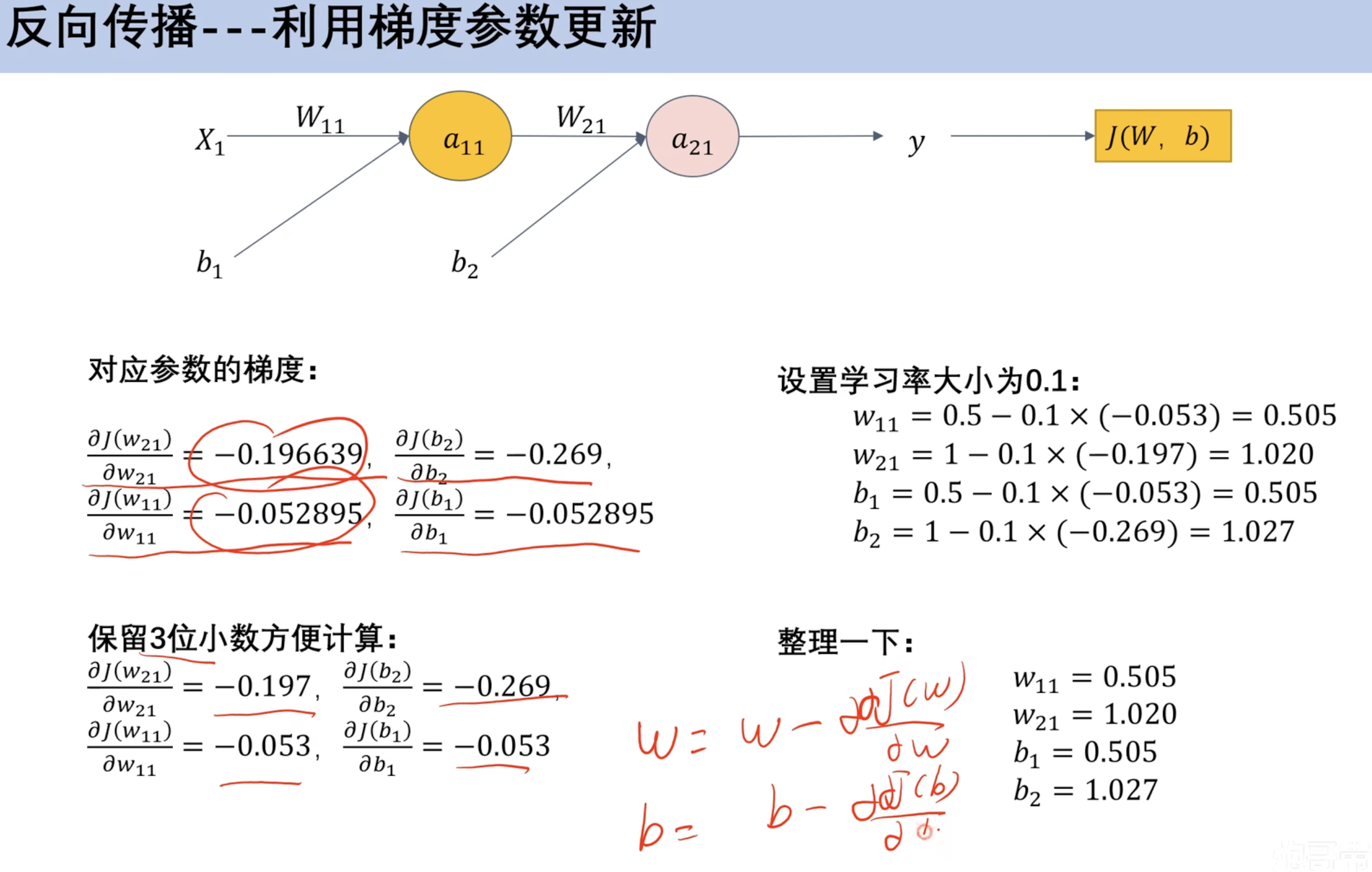
链式法则(数学补充) 单变量链式法则 多变量链式发展 ==反向传播== 案例 求解参数梯度 利用梯度参数更新
新参数前向传播 案例(预测乳腺癌 分类)
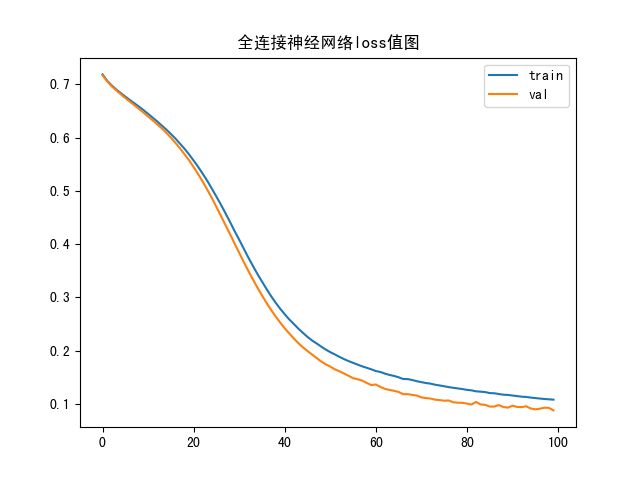
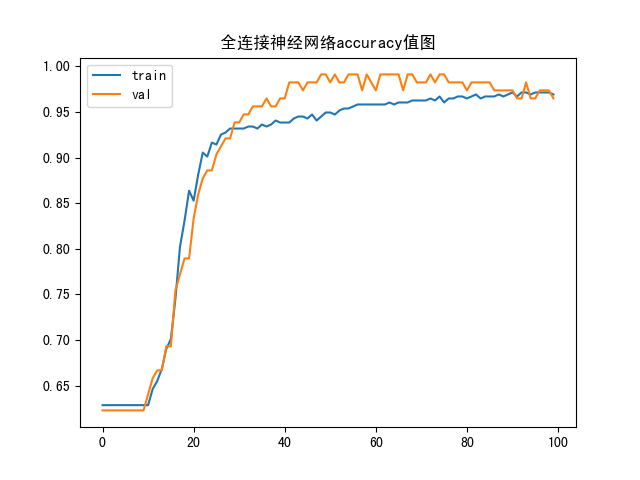
model_train 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitimport kerasfrom keras.layers import Dense from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categoricalfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report import matplotlib.font_manager as font_managerdataset = pd.read_csv("breast_cancer_data.csv" ) X = dataset.iloc[:, :-1 ] Y = dataset['target' ] x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2 , random_state=42 ) y_train_one = to_categorical(y_train, 2 ) y_test_one = to_categorical(y_test, 2 ) sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0 , 1 )) x_train = sc.fit_transform(x_train) x_test = sc.fit_transform(x_test) model = keras.Sequential() model.add(Dense(10 , activation='relu' )) model.add(Dense(10 , activation='relu' )) model.add(Dense(2 , activation='softmax' )) model.compile (loss='categorical_crossentropy' , optimizer='SGD' , metrics=['accuracy' ]) history = model.fit(x_train, y_train_one, epochs=120 , batch_size=64 , verbose=2 , validation_data=(x_test, y_test_one)) model.save('model.h5' ) plt.plot(history.history['loss' ], label='train' ) plt.plot(history.history['val_loss' ], label='val' ) plt.title("全连接神经网络loss值图" ) plt.legend() plt.show() plt.plot(history.history['accuracy' ], label='train' ) plt.plot(history.history['val_accuracy' ], label='val' ) plt.title("全连接神经网络accuracy值图" ) plt.legend() plt.show()
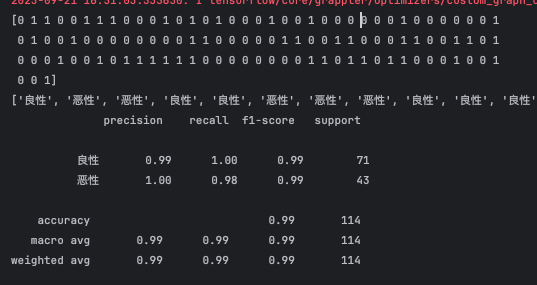
model_test 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 from cProfile import labelimport numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitimport kerasfrom keras.layers import Dense from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categoricalfrom sklearn.metrics import classification_report import matplotlib.font_manager as font_managerfrom keras.models import load_modeldataset = pd.read_csv("breast_cancer_data.csv" ) X = dataset.iloc[:, :-1 ] Y = dataset['target' ] x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2 , random_state=42 ) y_test_one = to_categorical(y_test, 2 ) sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0 , 1 )) x_test = sc.fit_transform(x_test) model = load_model("model.h5" ) predict = model.predict(x_test) y_pred = np.argmax(predict, axis=1 ) print (y_pred) result = [] for i in range (len (y_pred)): if y_pred[i] == 0 : result.append("良性" ) else : result.append("恶性" ) print (result)report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred, labels=[0 , 1 ], target_names=["良性" , "恶性" ]) print (report)
函数图像 loss
accuracy
预测报告
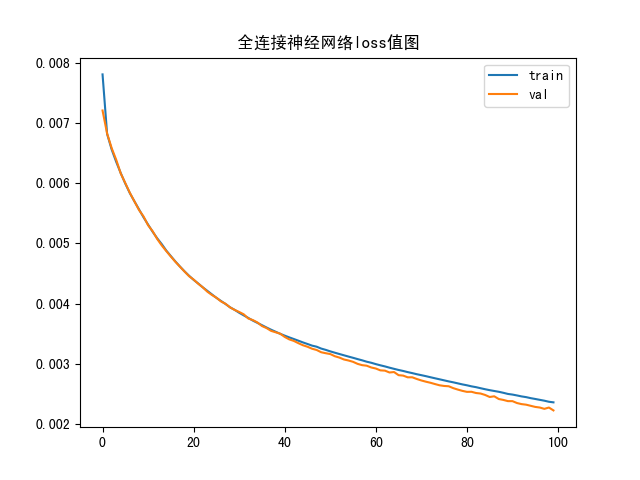
案例(空气质量 线性回归) model_train 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitimport kerasfrom keras.layers import Dense from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categoricaldataset = pd.read_csv("data.csv" ) sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0 , 1 )) scaled = sc.fit_transform(dataset) dataset_sc = pd.DataFrame(scaled) print (dataset_sc)X = dataset_sc.iloc[:, :-1 ] Y = dataset_sc.iloc[:, -1 ] x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.2 , random_state=42 ) model = keras.Sequential() model.add(Dense(10 , activation='relu' )) model.add(Dense(10 , activation='relu' )) model.add(Dense(1 )) model.compile (loss='mse' , optimizer='SGD' ) history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=100 , batch_size=32 , verbose=2 , validation_data=(x_test, y_test)) model.save('model.h5' ) plt.plot(history.history['loss' ], label='train' ) plt.plot(history.history['val_loss' ], label='val' ) plt.title("全连接神经网络loss值图" ) plt.legend() plt.show()
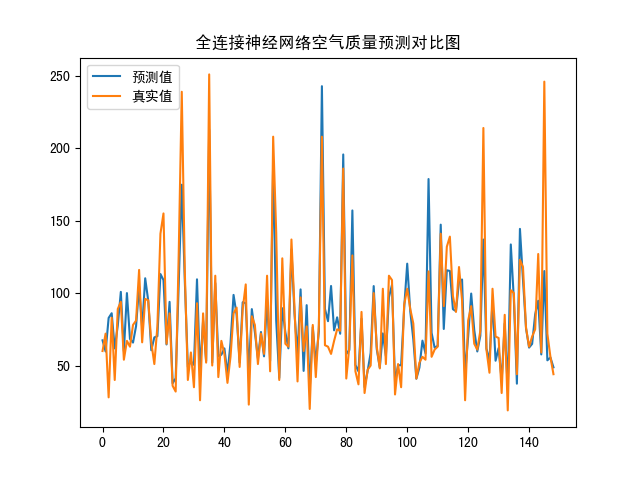
model_test 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 import numpy as npimport pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom scipy.ndimage import labelfrom sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScalerfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitimport kerasfrom keras.layers import Dense from keras.utils.np_utils import to_categoricalfrom keras.models import load_modelfrom math import sqrtfrom numpy import concatenatefrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_errordataset = pd.read_csv("data.csv" ) sc = MinMaxScaler(feature_range=(0 , 1 )) scaled = sc.fit_transform(dataset) dataset_sc = pd.DataFrame(scaled) X = dataset_sc.iloc[:, :-1 ] Y = dataset_sc.iloc[:, -1 ] x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, Y, test_size=0.05 , random_state=42 ) model = load_model("model.h5" ) yhat = model.predict(x_test) inv_yhat = concatenate((x_test, yhat), axis=1 ) inv_yhat = sc.inverse_transform(inv_yhat) prediction = inv_yhat[:, 6 ] y_test = np.array(y_test) y_test = np.reshape(y_test, (y_test.shape[0 ], 1 )) inv_y = concatenate((x_test, y_test), axis=1 ) print (inv_y)inv_y = sc.inverse_transform(inv_y) real = inv_y[:, 6 ] print (real)remse = sqrt(mean_squared_error(real, prediction)) mape = np.mean(np.abs (real - prediction) / real) print ("remse" , remse)print ("mape" , mape)plt.plot(prediction, label="预测值" ) plt.plot(real, label="真实值" ) plt.title("全连接神经网络空气质量预测对比图" ) plt.legend() plt.show()
loss图像
真实值预测值对比图