单链表 存储方式
idx 表示结点编号
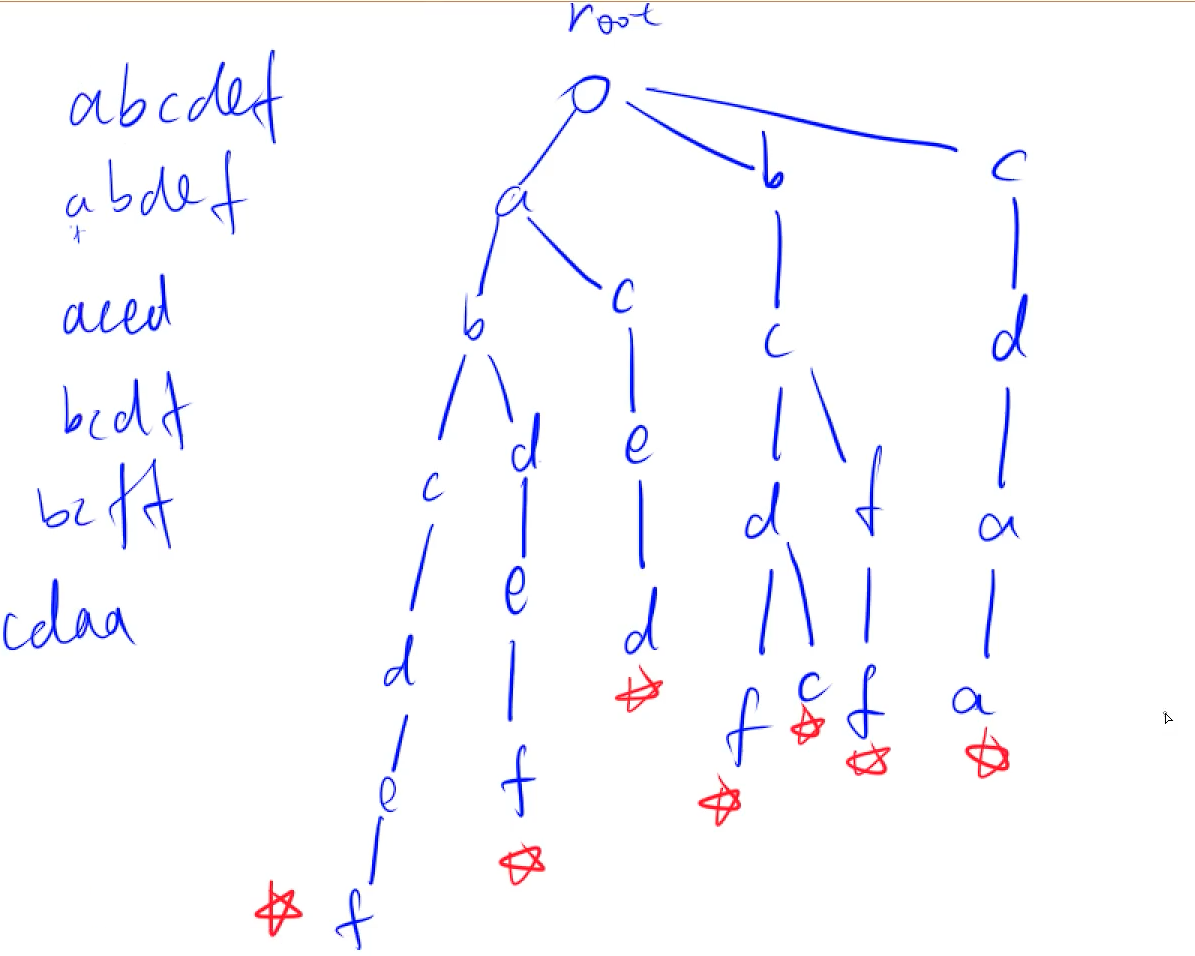
Trie 概念
存储
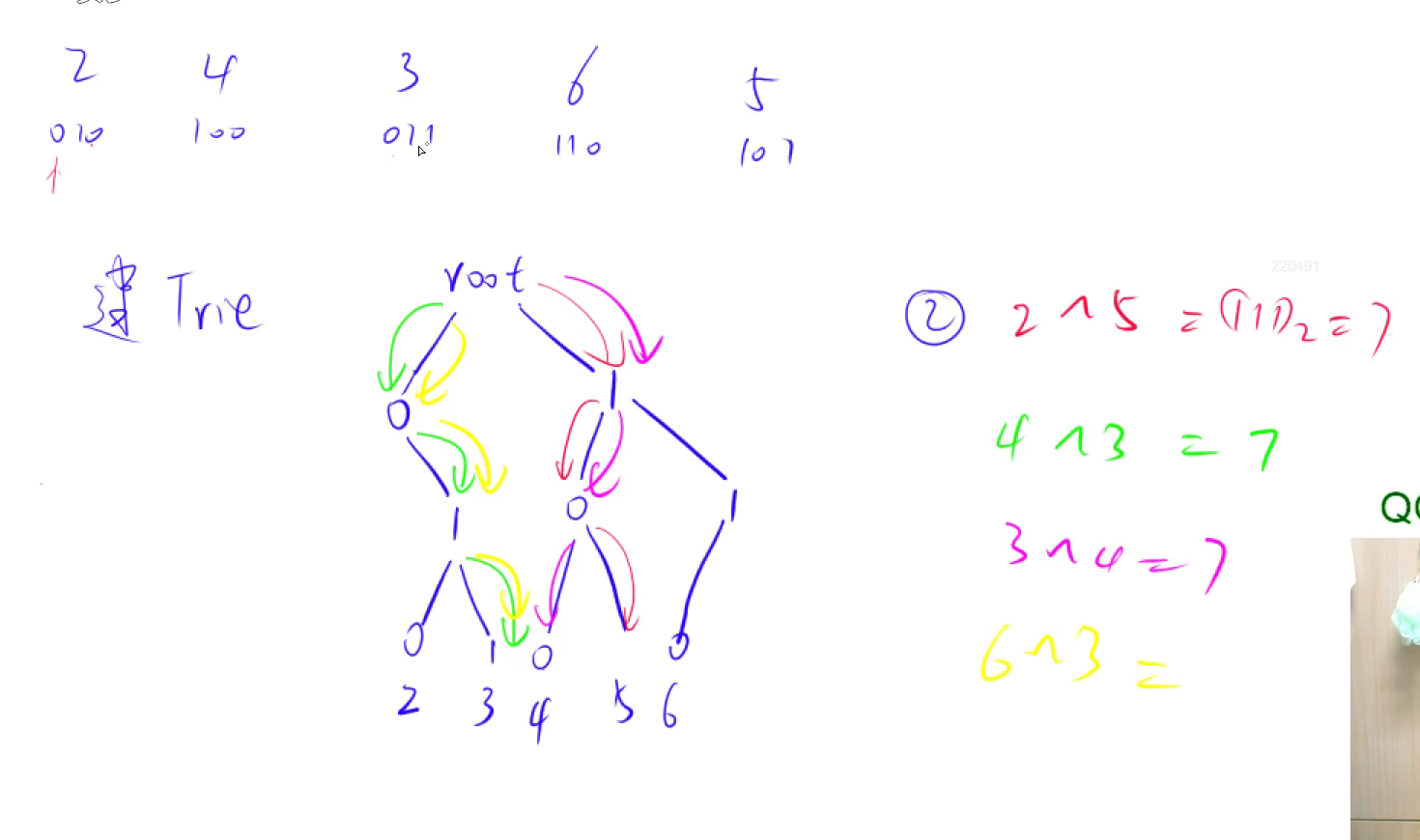
acwing143.最大异或对
思路: 1.将每个数放在树中
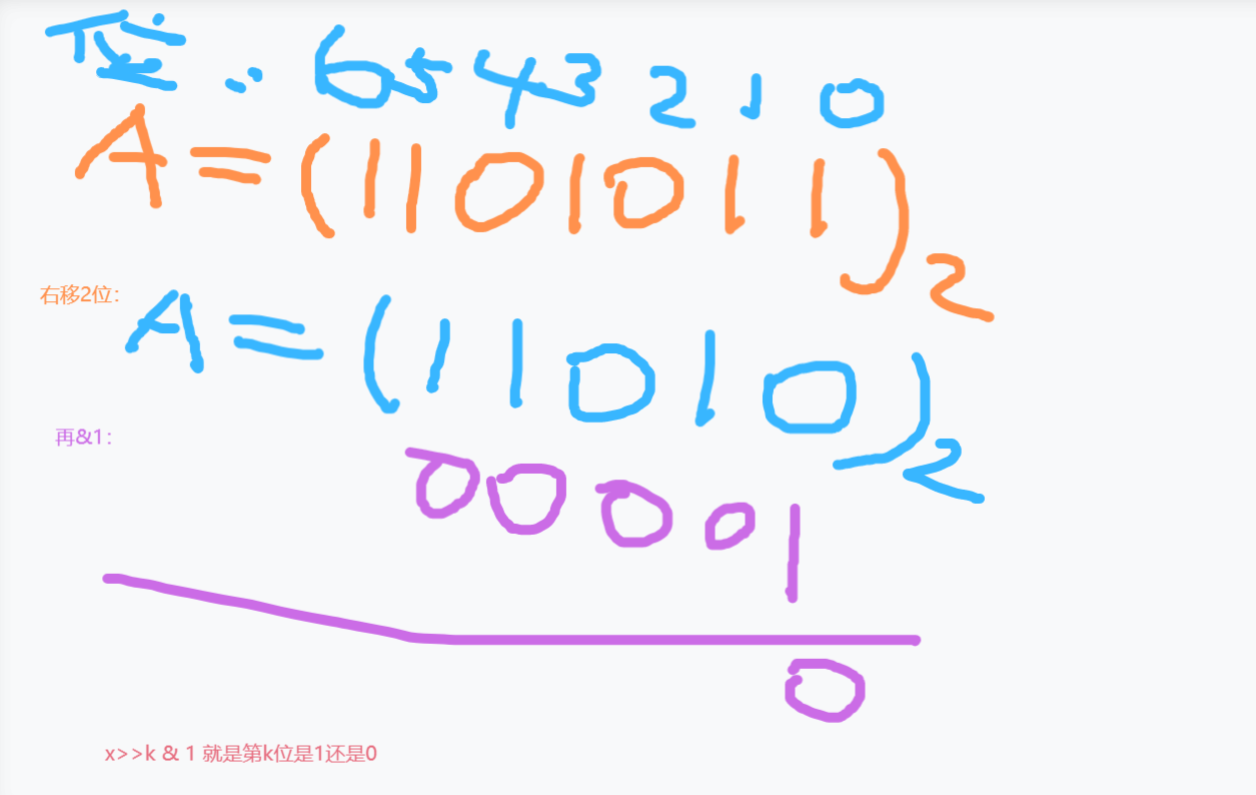
2.遍历一遍数据,从 31 位开始 是 1 找 0 是 0 找 1 没有则只能找当前相同 通过 res +=1<<i; 得到答案
移位操作 预处理数据为二进制 x >> k & 1
代码: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N = 100010 , M = 3e7 ;int son[M][2 ], idx;int a[N];int insert (int x) int p = 0 ; for (int i = 30 ; ~i; i--) { int &s = son[p][x >> i & 1 ]; if (!s) s= ++idx; p = s; } } int query (int x) int p = 0 , res = 0 ; for (int i = 30 ; ~i ; i--){ int s = x >> i & 1 ; if (son[p][!s]) { res += 1 << i; p=son[p][!s]; } else p=son[p][s]; } return res; } int main () int n,res=0 ; cin >> n; for (int i = 0 ; i < n;i++){ cin >> a[i]; insert (a[i]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) res=max (res,query (a[i])); cout << res; return 0 ; }
line9:>=0 可以用 ~i 表示
line10,通过左值引用得到数组的值 对 s 修改便修改数组元素的值
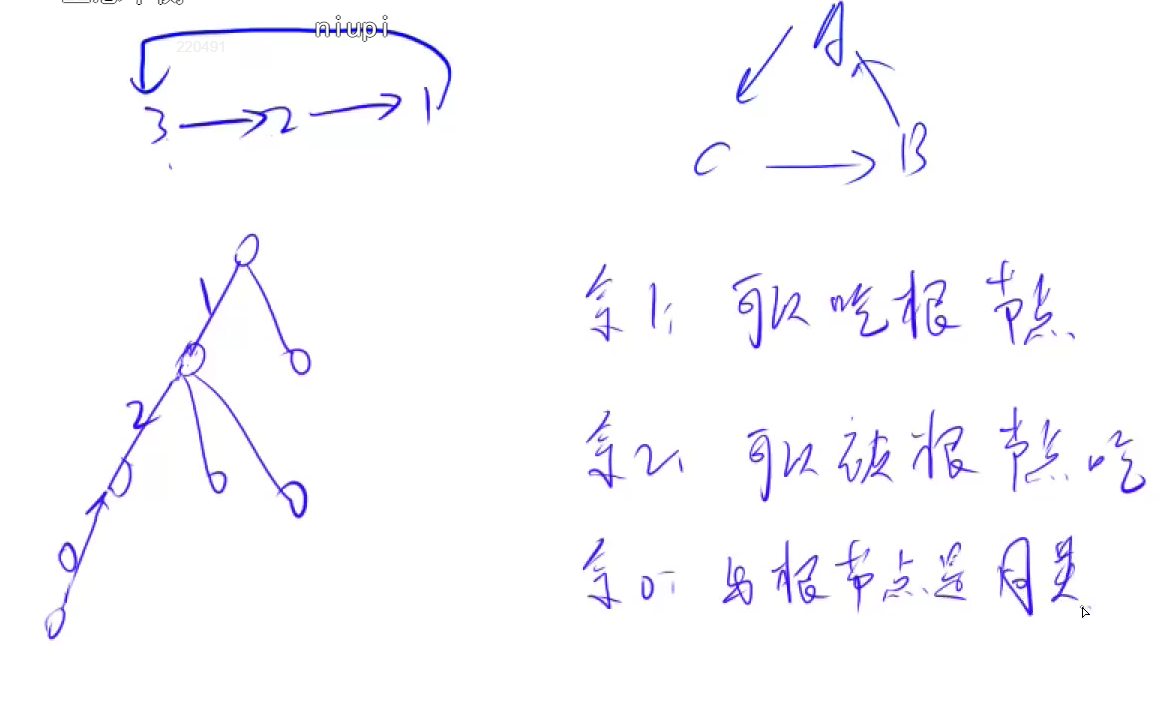
并查集 概念作用: 1.将两个集合合并 (近乎 O(1)复杂度)
2.询问两个元素是否在一个结合中
结构样图:
基本问题:
acwing836 集合合并: 题目
代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <iostream> using namespace std;const int N=100010 ;int pre[N];int n, m;int find (int x) if (find (x)!=pre[x]) pre[x] = find (pre[x]); return pre[x]; } int main () cin>>n >> m; for (int i = 0 ; i <= n;i++) pre[i]=i; while (m--){ char op[2 ]; int a, b; cin >> op >> a >> b; if (op[0 ]=='M' ) pre[find (a)]==find (b); if (op[0 ]=='Q' ){ if (find (a)==find (b)) cout << "Yes" << endl; else cout << "No" << endl; } } return 0 ; }
注: 1.数组 1~n 索引值 pre[i]=i i 是 n 个数 pre[i]表示自己的父亲
2.find 路径压缩 :使一个集合中的父亲公共一个 近乎 O(1) 复杂度
acwing837 连通块中点的数量: 题目:
代码: 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;const int N = 100010 ;int p[N], size1[N];int n, m;int find (int x) if (p[x] != x) x = p[x]; return p[x]; } int main () cin >> n >> m; for (int i= 1 ; i <= n;i++) { p[i]=i; size1[i]=1 ; } while (m--){ char op[5 ]; int a, b; cin >> op; if (op[0 ]=='C' ) { cin >> a >> b; if (find (a)==find (b)) continue ; size1[find (b)] += size1[find (a)]; p[find (a)] = find (b); } else if (op[1 ]=='1' ){ cin >> a >> b; if (find (a)==find (b)) cout << "Yes" << endl; else cout << "No" << endl; } else { cin >> a; cout << size1[find (a)]<<endl; } } return 0 ; }
注: 1.最后 3 查找该集合个数,以 size1 数组初始化每个集合个数为 1,
2.size1[find(b)] += size1[find(a)]; 把 a 插入到 b 下 b 的个数+=a 的个数
3.对应的:p[find(a)] = find(b); 把 a 插入到 b 下
食物链 题目: 思路:
哈希表
1e9 个数据 映射成 1e5
可能会引起冲突 通过一下两种方法解决
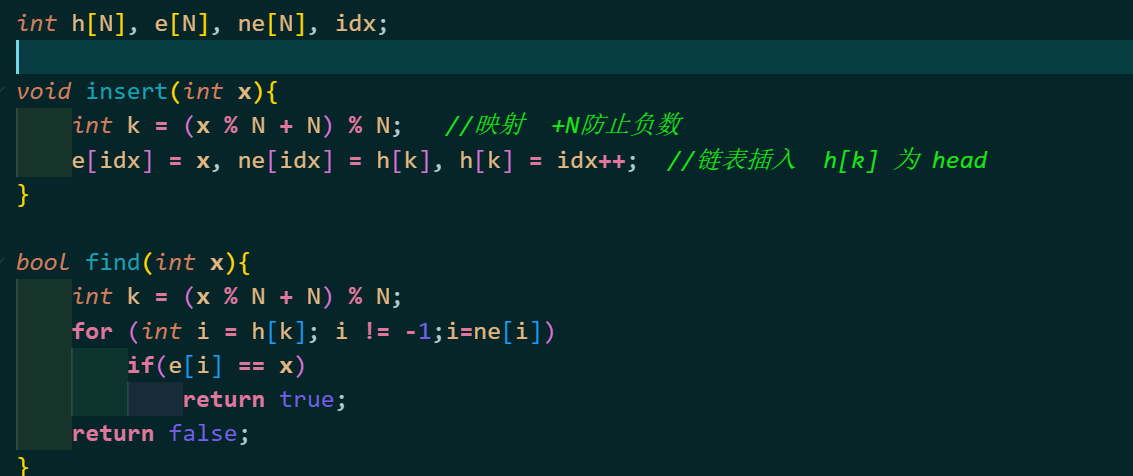
拉链法
开一个数组 1e5
若 11 23 映射到 3 , 3 下开一个单链表
insert 1 2 3 4 void insert (int x) int k = (x % N + N) % N; e[idx] = x, ne[idx] = h[k], h[k] = idx++; }
find 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 bool find (int x) int k = (x % N + N) % N; for (int i = h[k]; i != -1 ;i=ne[i]) if (e[i] == x) return true ; return false ; }
开放寻址法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 const int N = 200003 , null = 0x3f3f3f ; int h[N];int find (int x) int k = (x % N + N) % N; while (h[k] != null && h[k] != x){ k++; if (k==N) k=0 ; } return k; }
👀 字符串哈希
将字符串 前缀哈希值 1,2,3,4… 得到 1 - n 的哈希值
字符串转为 p 进制数
然后 mod 2^64 这里采用 unsigned ll 存储 溢出自动 mod
注: 不能映射成 0
经验规律: p =131 或 1333 1 Q= 2^64;
用 unsigned long long 存储 h,溢出相当于% Q;
求 L 到 R 的哈希值
前缀哈希:h[i]=h[i-1]*p +str[i]
L-R 哈希公式: h[R] - h[L] * P^(R-L+1)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std;typedef unsigned long long ULL;const int N = 100010 ,P=131 ;int n, m;char str[N];ULL h[N], p[N]; ULL get (int l,int r) { return h[r] - h[l - 1 ] * p[r - l + 1 ]; } int main () cin >> n >> m >> str + 1 ; p[0 ] = 1 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n;i++) { p[i] = p[i - 1 ] * P; h[i] = h[i - 1 ] * P + str[i]; } while (m--){ int l1, r1, l2, r2; cin >> l1 >> r1 >> l2 >> r2; if (get (l1,r1) == get (l2,r2)) cout << "Yes" << endl; else cout << "No" << endl; } return 0 ; }



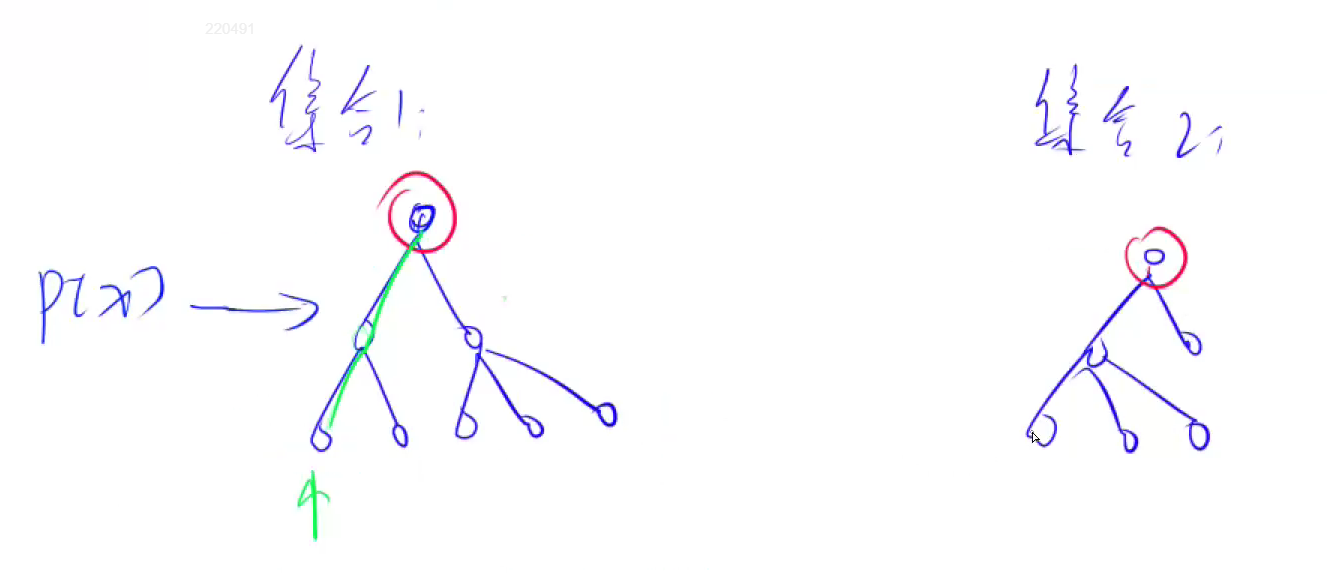






 1. 将 L -> 1 左移 扩大 至和 R 对齐
1. 将 L -> 1 左移 扩大 至和 R 对齐