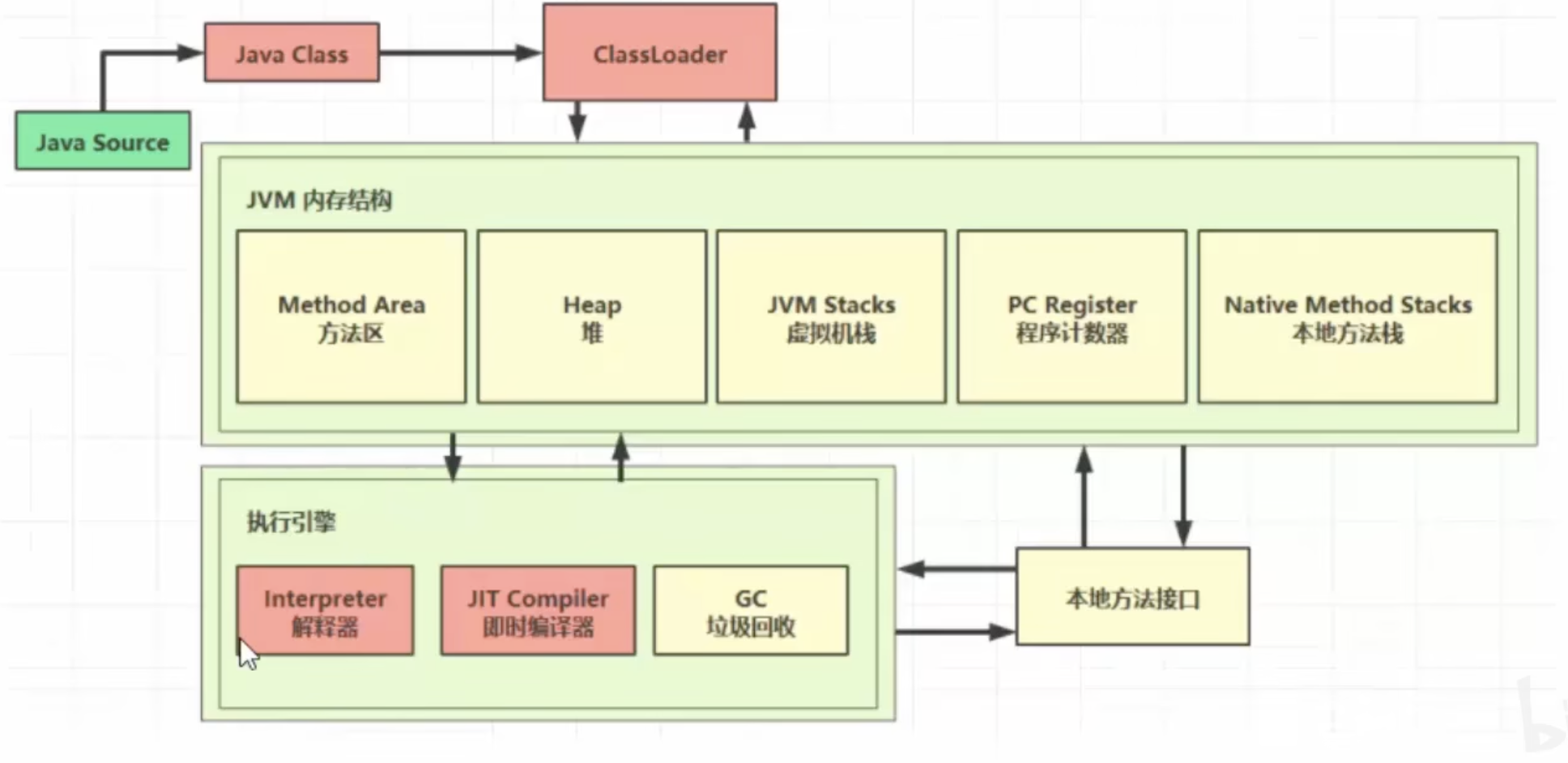
JVM-1.内存结构
引言
什么是JVM
- 定义:
- Java Virtual Machine - java 程序的运行环境(java 二进制字节码的运行环境)
- 好处:
- 一次编写,到处运行
- 自动内存管理,垃圾回收功能
- 数组下标越界检查 多态 比较: jvm jre jdk
- 多态
- 比较:
jvm jre jdk- 基础类库:
IO List等 - 编译工具:
javac 内存监测工具 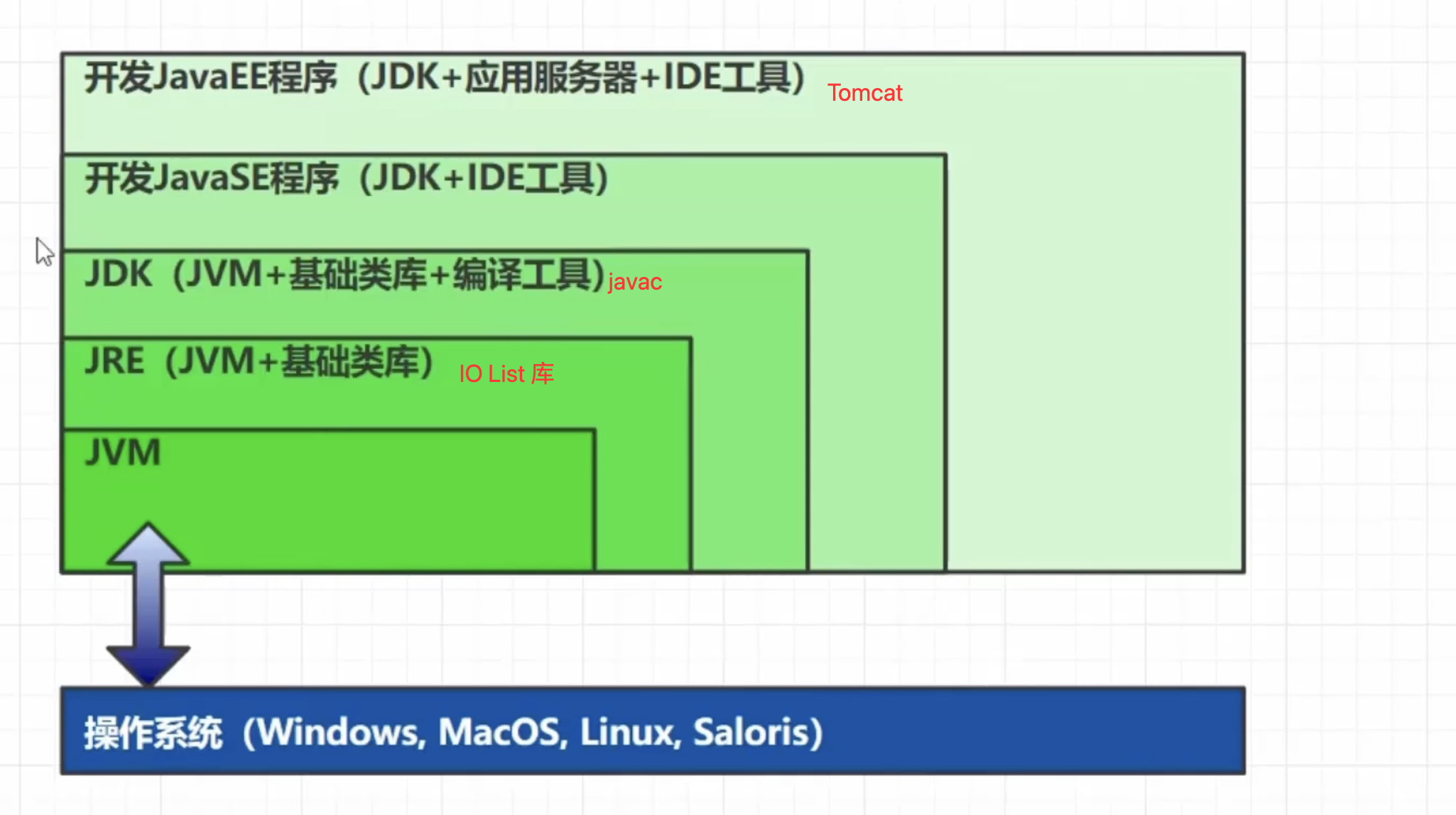
- 基础类库:
学jvm有什么用
- 面试
- 理解底层的实现原理
- 中高级程序员的必备技能
常见的JVM
- jVM是一种规范
- 实现很多
- 本课程讲hotspot
学习路线
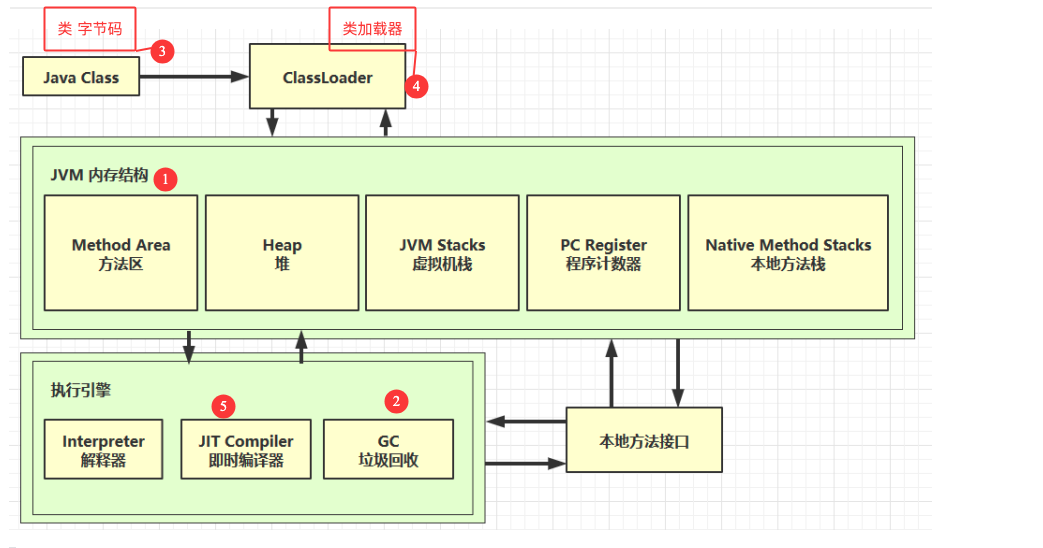
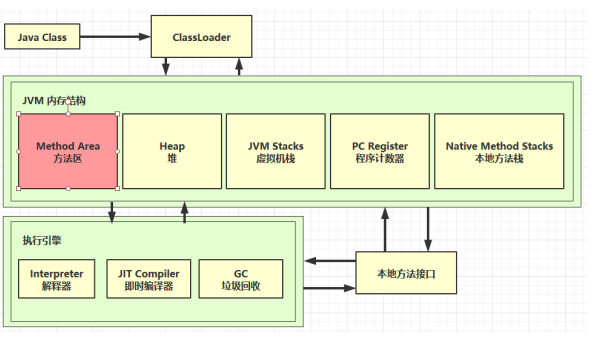
一、内存结构
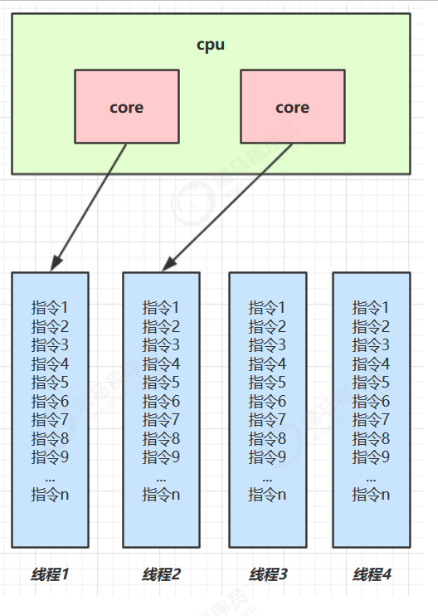
1. 程序计数器
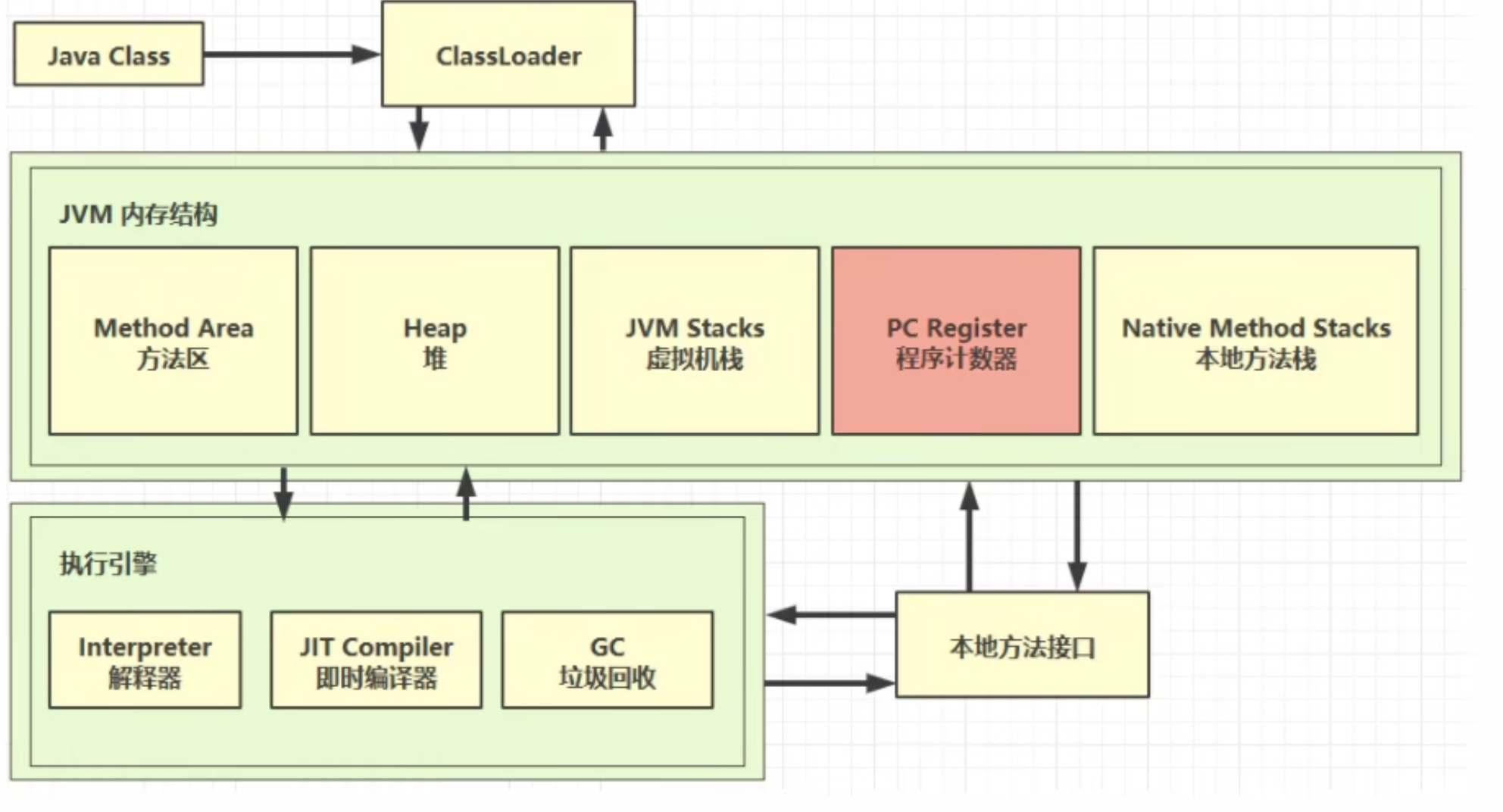
1.1 定义
Program Counter Register 程序计数器(寄存器)
- 作用
- 是记住
下一条jvm指令的执行地址
- 是记住
- 特点
- 是线程私有的 (每个线程有属于自己的程序计数器)
- 不会存在内存溢出
唯一一个不会内存溢出的地方
1.2 作用
- 通过寄存器(CPU组件)实现java程序计数器
- 屏蔽物理硬件

- 屏蔽物理硬件
2.虚拟机栈
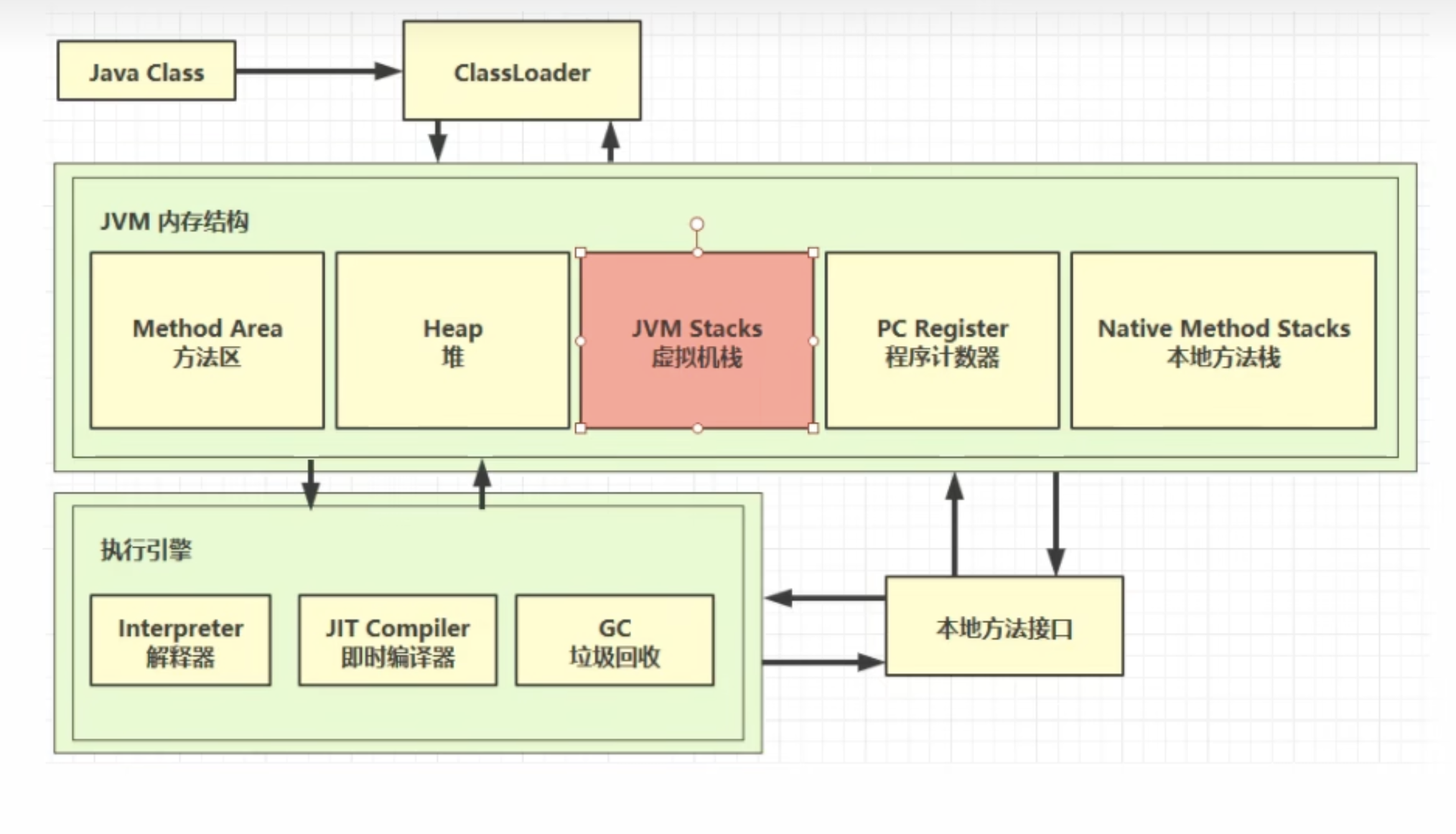
2.1 定义
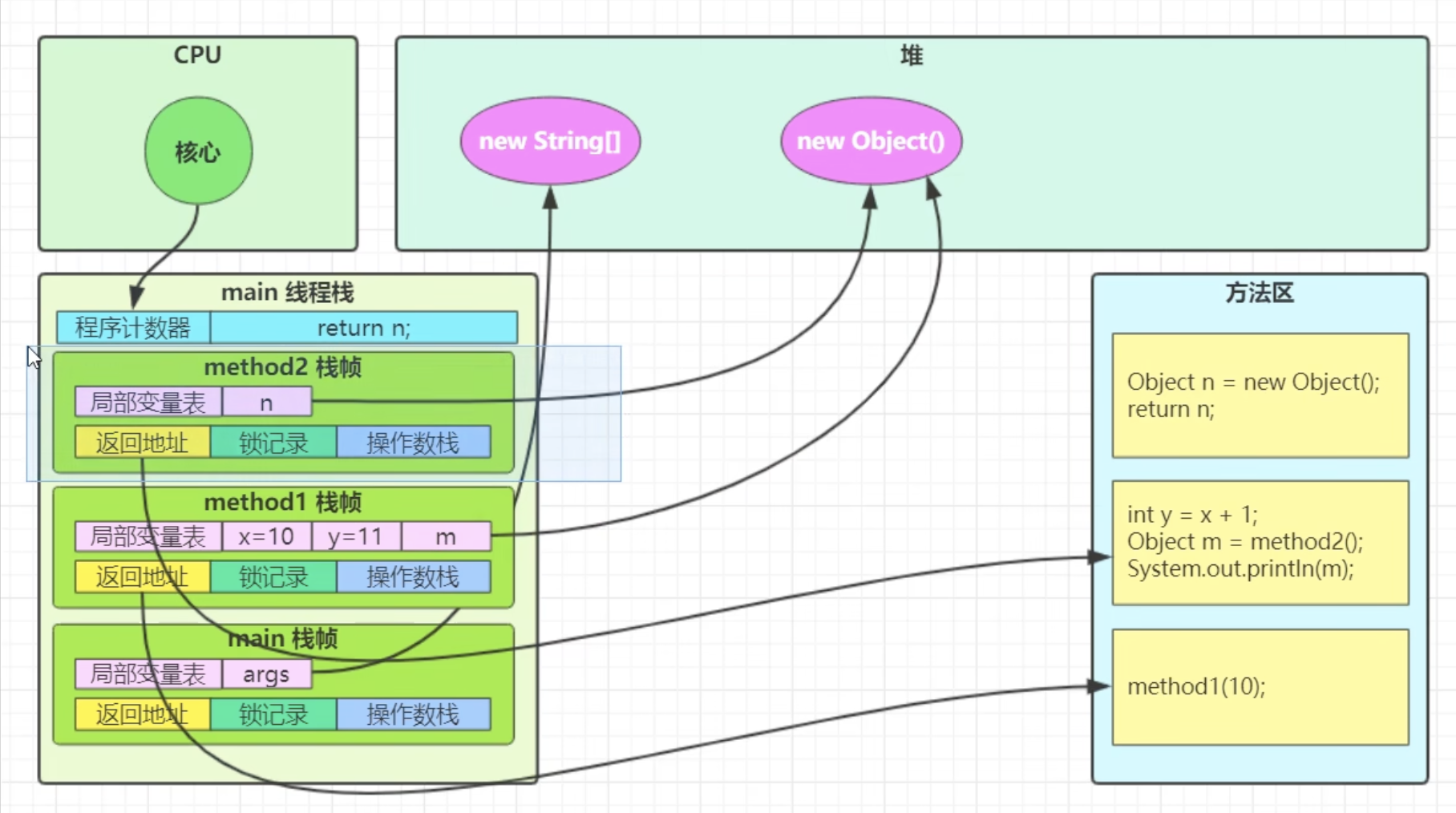
Java Virtual Machine Stacks (Java 虚拟机栈)- 每个线程运行时所需要的内存,称为虚拟机栈
- 每个栈由多个栈帧(Frame)组成,对应着每次方法调用时所占用的内存
- 每个线程只能有一个活动栈帧,对应着当前正在执行的那个方法
- 问题辨析:
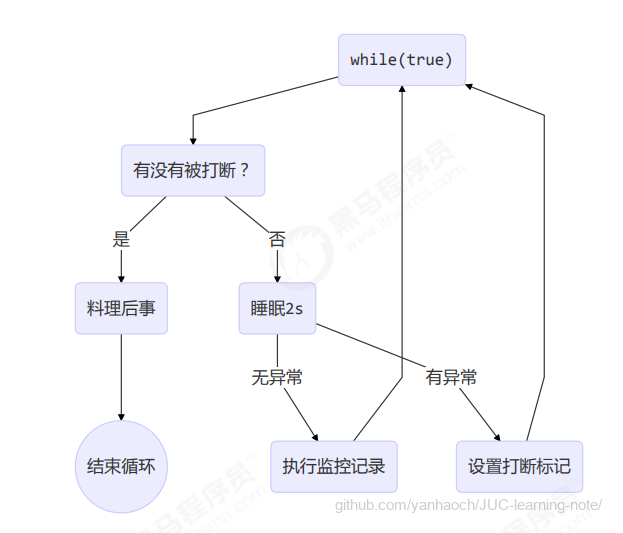
- 垃圾回收是否涉及栈内存?
不涉及,栈内存自动释放 - 栈内存分配越大越好吗?
-Xss指定大小 默认1024kb 越大线程越少 - 方法内的局部变量是否线程安全?
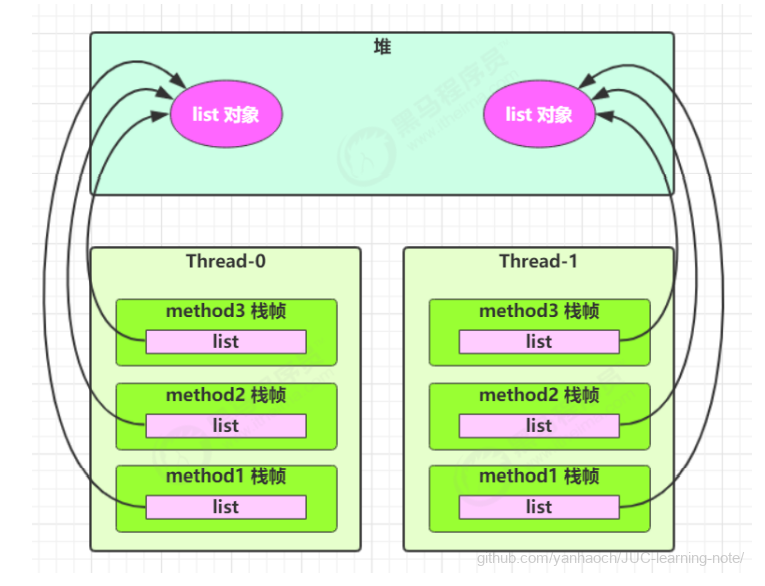
- 如果方法内局部变量没有逃离方法的作用访问,它是线程安全的
- 如果是局部变量引用了对象,并逃离方法的作用范围,需要考虑线程安全
如static全局变量
- 垃圾回收是否涉及栈内存?
demo: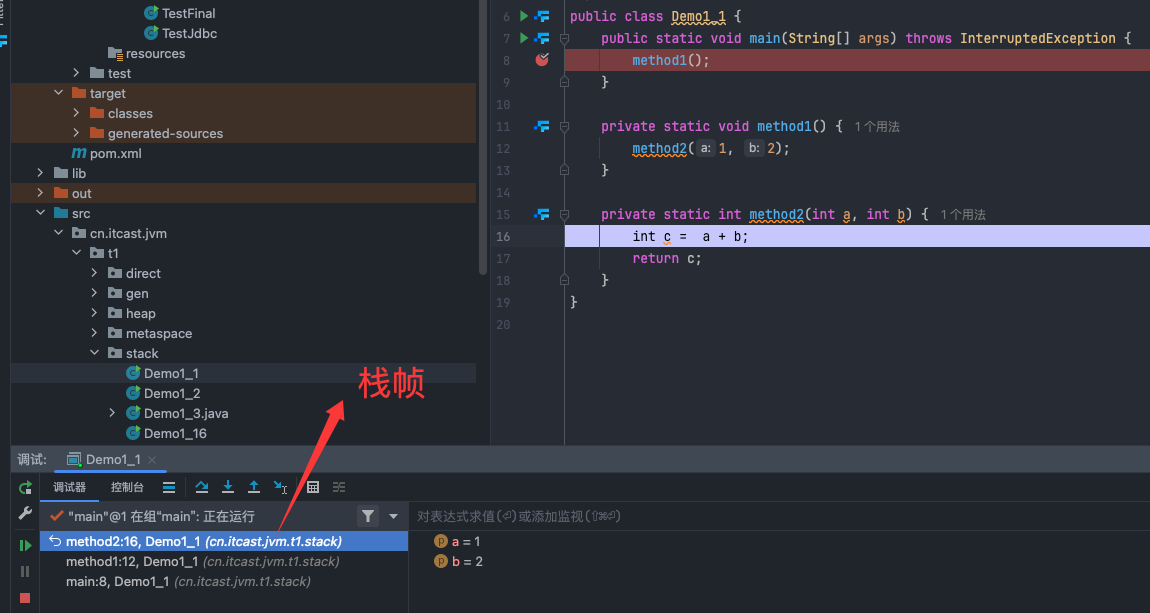
2.2 栈内存溢出
- 栈帧过多导致栈内存溢出
- 栈帧过大导致栈内存溢出
- 演示
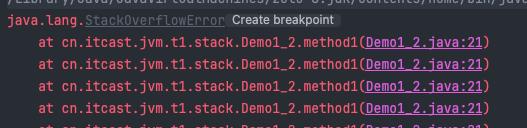
- 执行了
42171次
1 | /** |
循环依赖问题:
- 原因:
- 部门下有员工,
员工属性有部门,部门下有员工 - 无限套娃
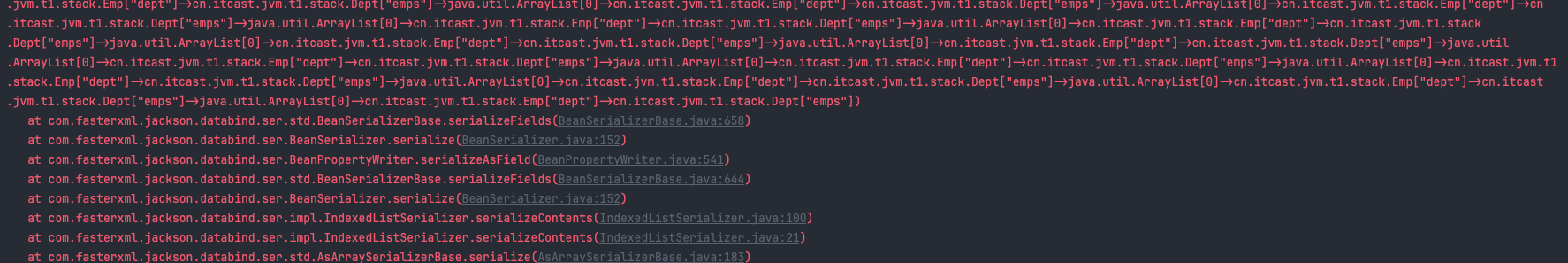
- 部门下有员工,
- 如何正确使用:
- 在员工下的部门加上
@JsonIgnore 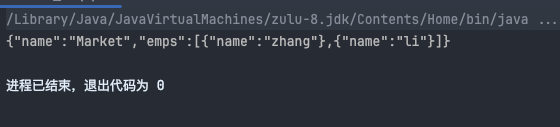
- 在员工下的部门加上
1 | /** |
2.3 线程运行诊断
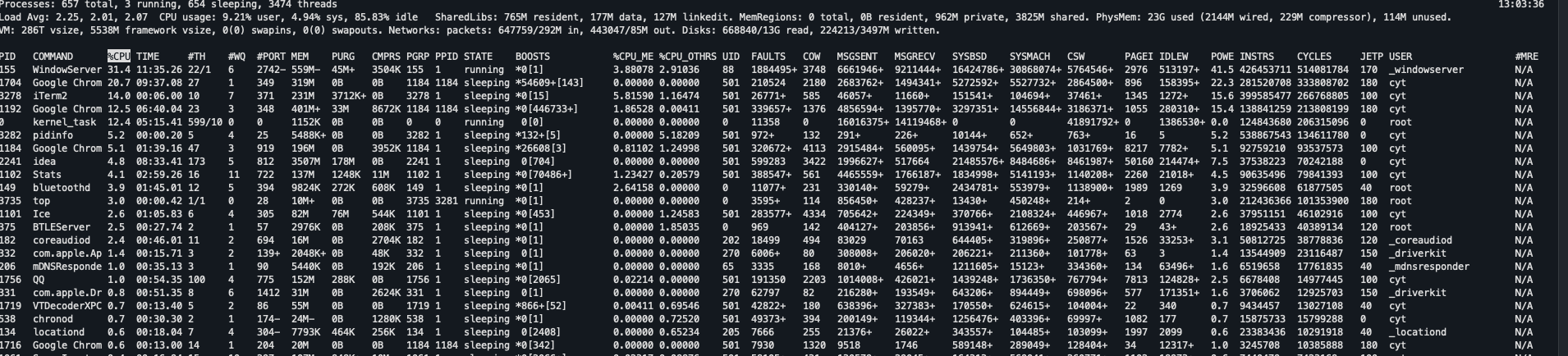
案例1:cpu 占用过多
nohup java Dem1_16 &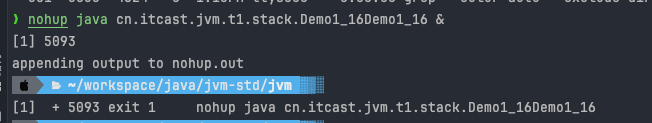
定位
- 用top定位哪个进程对cpu的占用过高
ps H -eo pid,tid,%cpu | grep 进程id(用ps命令进一步定位是哪个线程引起的cpu占用过高)jstack 进程id- 可以根据线程id 找到有问题的线程,进一步定位到问题代码的源码行号
- 用top定位哪个进程对cpu的占用过高
案例2:程序运行很长时间没有结果 (死锁)
3. 本地方法栈
- 用C语言写的native方法,直接和底层交互
- 举例 Object类下的方法

protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException;
4. 堆
- 上面三个线程私有
堆和方法区线程共享
4.1 定义
- Heap 堆
- 通过 new 关键字,创建对象都会使用堆内存
- 特点
- 它是线程共享的,
- 堆中对象都需要考虑线程安全的问题 有垃圾回收机制
4.2 堆内存溢出
- 控制堆空间参数:
-Xmx8m 

1 | /** |
4.3 堆内存诊断
jps工具- 查看当前系统中有哪些 java 进程
jmap工具- 查看堆内存占用情况 jmap - heap 进程id
- 只能查看某一时刻

jconsole工具- 图形界面的,多功能的监测工具,可以连续监测
- 功能全 。终端输入
jconsole弹出选择框选择java类 
- 案例 垃圾回收后,内存占用仍然很高
jvisualvm终端输入
1 | /** |
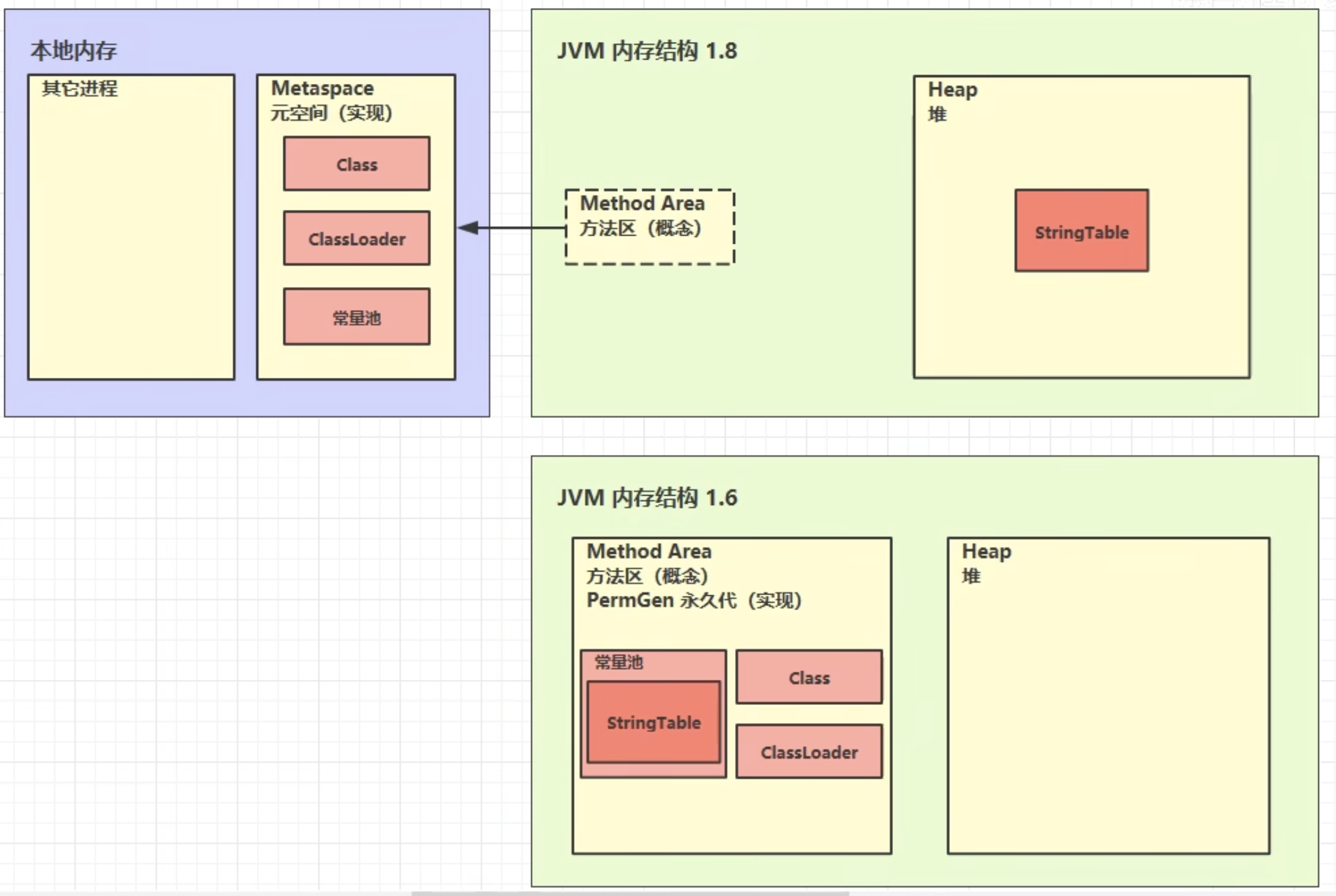
5. 方法区
5.1 定义
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/specs/jvms/se8/html/jvms-2.html
The Java Virtual Machine has a method area that is shared among all Java Virtual Machine threads. The method area is analogous to the storage area for compiled code of a conventional language or analogous to the “text” segment in an operating system process. It stores per-class structures such as the run-time constant pool, field and method data, and the code for methods and constructors, including the special methods (§2.9) used in class and instance initialization and interface initialization.
Java 虚拟机具有在所有 Java 虚拟机线程之间共享的方法_区域_ 。方法区域类似于常规语言的编译代码的存储区域,或类似于作系统进程中的“文本”段。它存储每个类的结构,例如运行时常量池、字段和方法数据,以及方法和构造函数的代码,包括类和实例初始化中使用的特殊方法 (§2.9) 和接口初始化。
The method area is created on virtual machine start-up. Although the method area is logically part of the heap, simple implementations may choose not to either garbage collect or compact it. This specification does not mandate the location of the method area or the policies used to manage compiled code. The method area may be of a fixed size or may be expanded as required by the computation and may be contracted if a larger method area becomes unnecessary. The memory for the method area does not need to be contiguous.
方法区域在虚拟机启动时创建。尽管方法区域在逻辑上是堆的一部分,但简单的实现可以选择不进行垃圾回收或压缩。此规范不强制要求方法区域的位置或用于管理编译代码的策略。方法区域可以是固定大小的,也可以根据计算的需要进行扩展,如果不需要更大的方法区域,则可以收缩。方法区域的内存不需要是连续的。
5.2 组成
- 1.6用
永久代 - 1.8用
元空间
5.3 方法区内存溢出
- 1.8 以前会导致永久代内存溢出
- `* 演示永久代内存溢出 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen space *
-XX:MaxPermSize=8m
- 1.8 之后会导致元空间内存溢出
* 演示元空间内存溢出 java.lang.OutOfMemoryError: Metaspace* -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize=8m
案例:
1 | /** |
场景:
- 使用
cglibspringmybatis
5.4 运行时常量池
- 常量池,就是一张表,虚拟机指令根据这张常量表找到要执行的类名、方法名、参数类型、字面量 等信息
- 运行时常量池,常量池是 *.class 文件中的,当该类被加载,它的常量池信息就会放入运行时常量 池,并把里面的符号地址变为真实地址
- 执行
javap -v如下
1 | ❯ javap -v out.production.jvm.cn.itcast.jvm.t5.HelloWorld |
5.5 StringTable
先看几道面试题:
案例解析
1 | // 串池(类似哈希表) StringTable [ "a", "b" ,"ab" ] hashtable 结构,不能扩容 |
javac -g Demo1_22.java- 编译期优化
- 可以发现s5在javac编译时已经赋值“ab”
- 此时“ab”已在串池中
1 | // |
javap -v Demo1_22.class > output.txt
1 | ❯ javap -v my1 |
5.5 StringTable特性
- 常量池中的字符串仅是符号,第一次用到时才变为对象
- 利用串池的机制,来避免重复创建字符串对象
字符串变量拼接的原理是 StringBuilder (1.8)字符串常量拼接的原理是编译期优化- 可以使用 intern 方法,主动将串池中还没有的字符串对象放入串池
1.8 将这个字符串对象尝试放入串池,如果有则并不会放入,如果没有则放入串池, 会把串 池中的对象返回- 1.6 将这个字符串对象尝试放入串池,如果有则并不会放入,如果没有会把此对象复制一份, 放入串池, 会把串池中的对象返回
1 | public class Demo1_23 { |
1 | public class Demo1_23 { |
面试题
1 | /** |
5.6 StringTable位置
演示代码:
1 | /** |
jdk1.6报错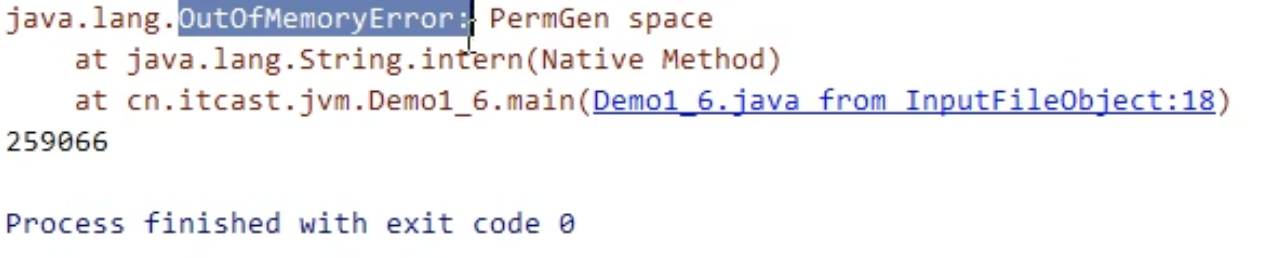
jdk1.8报错
5.7 StringTable 垃圾回收
- 代码
1 | /** |
- 日志
- 循环十万次,放入十万个数到
StringTable - 触发GC回收
GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4096K->496K(4608K)] 4096K->536K(15872K), - 并没有真正放入十万个数(53774个):
Number of entries : 53774 = 1290576 bytes, avg 24.000
- 循环十万次,放入十万个数到
1 | [GC (Allocation Failure) [PSYoungGen: 4096K->496K(4608K)] 4096K->536K(15872K), 0.0007230 secs] [Times: user=0.01 sys=0.00, real=0.00 secs] |
5.8 StringTable 性能调优
调整 -XX:StringTableSize=桶个数
- 案例代码
1 | /** |
- 默认
60013个
1 | cost:129 (时间 ms) |
- 修改为
200000个后- 时间为98ms
-XX:StringTableSize=200000- 原因:空间换时间
1 | cost:98 |
- 调小,修改为
1009个-XX:StringTableSize=1009- 时间明显变慢
- 原因:哈希冲突太多
1 | cost:1497 |
考虑将字符串对象是否入池
- 入池和不入池对内存占比
1 | /** |
- 使用
visualvm工具 - 读取文件之前

- 开始读文件
address.add(line);- 加起来占用
80%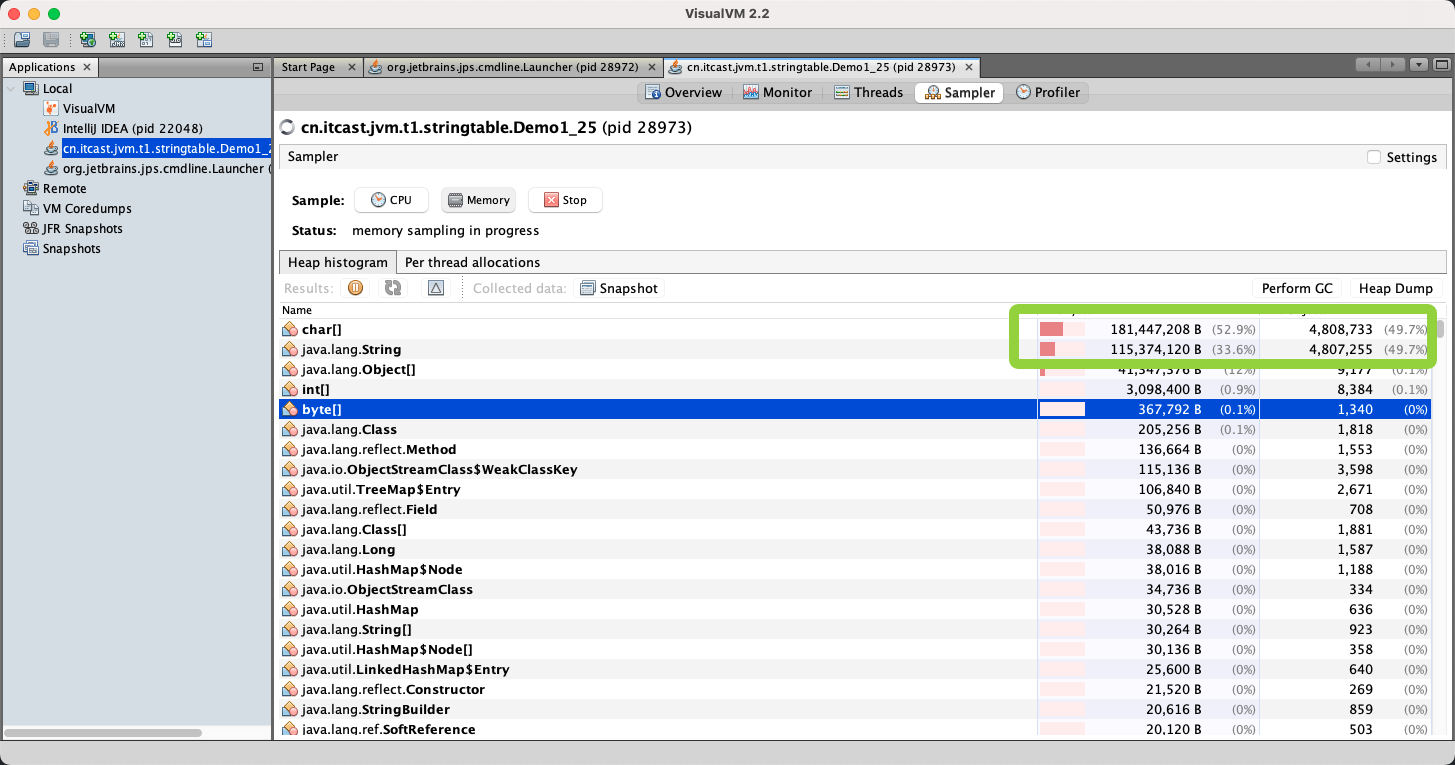
- 加起来占用
- 使用放入串池方法
address.add(line.intern());- 加起来占用
60%String和char[]
- 加起来占用
6. 直接内存
6.1 定义
Direct Memory
- 不属于jvm,是内存区域
- 常见于 NIO 操作时,
- 用于数据缓冲区 分配回收成本较高,
- 但读写性能高 不受 JVM 内存回收管理
案例
1 | /** |
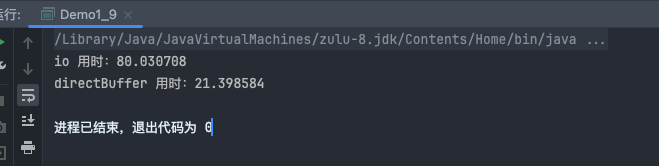
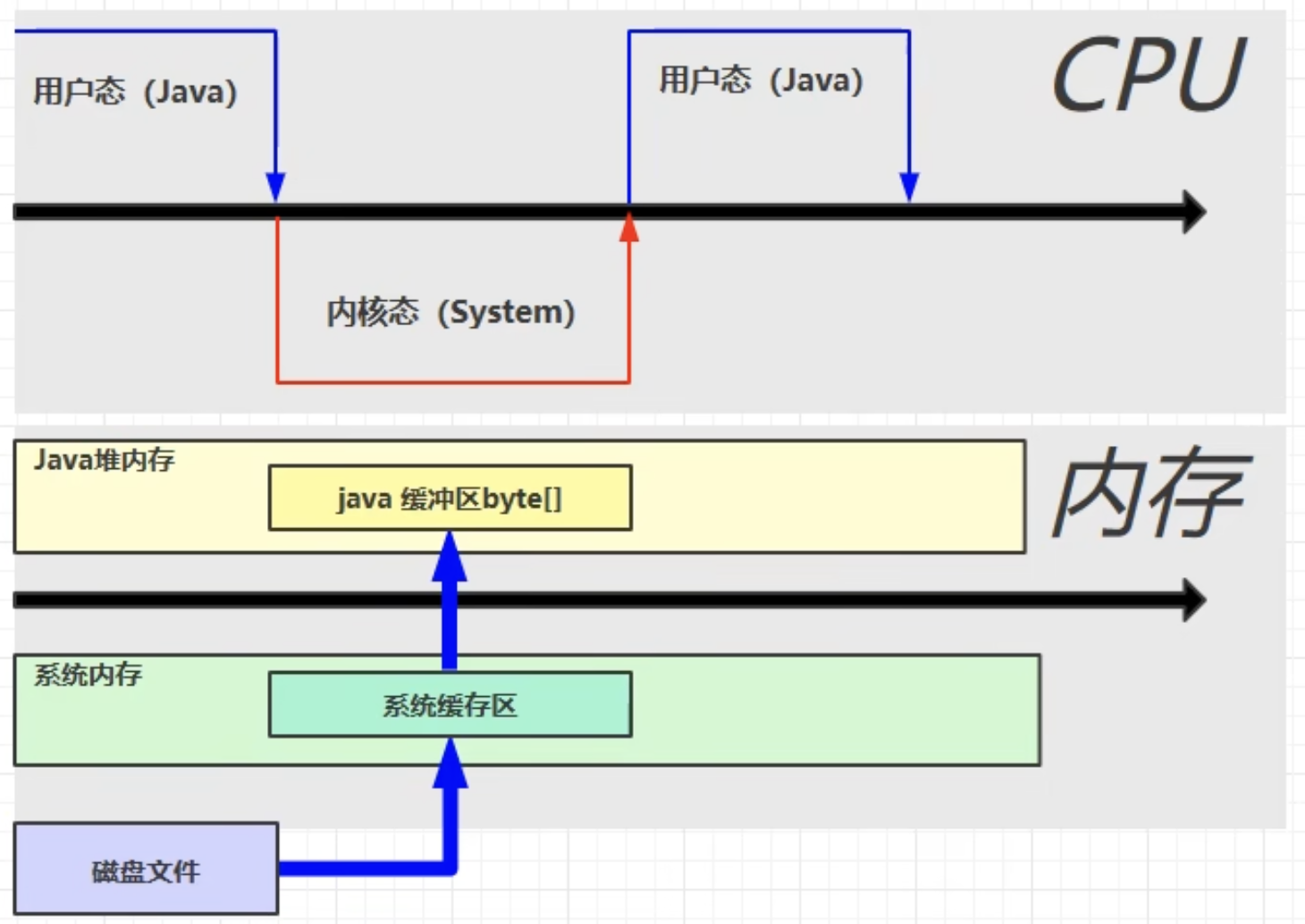
普通io:
- 切换为内核态
- 在内存申请java缓冲区
- 系统缓冲区内容复制到java缓冲区
directBuffer:
- 调用
ByteBuffer bb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1Mb); direct memoryjava和系统都可以直接访问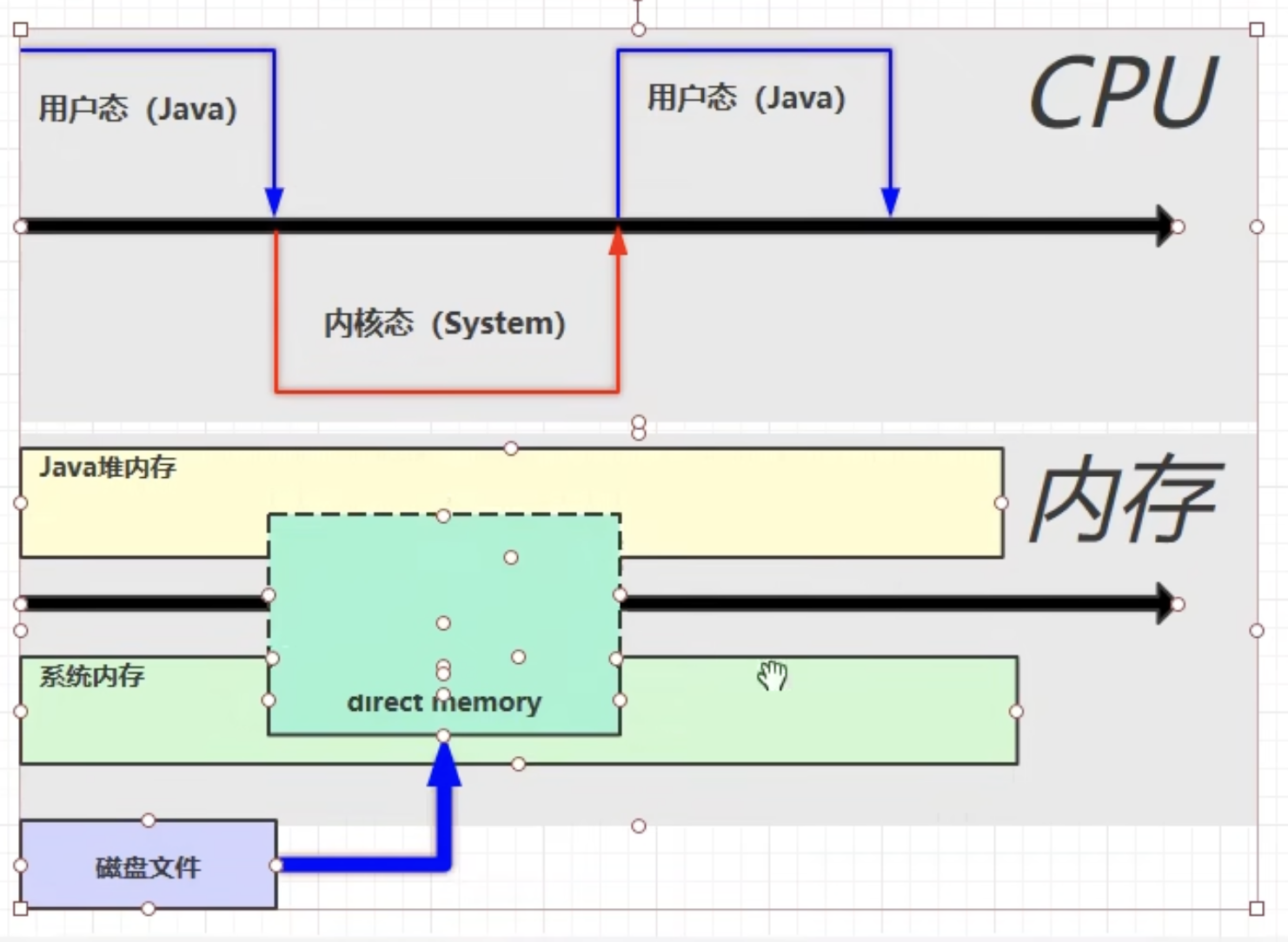
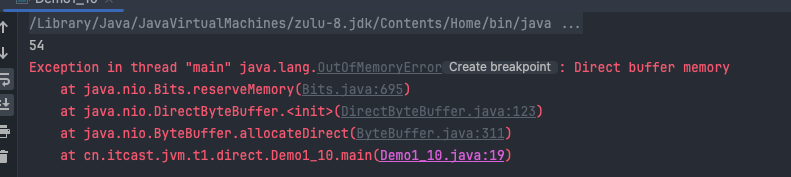
内存溢出
1 | /** |
6.2 分配和回收原理
- 使用了
Unsafe对象完成直接内存的分配回收,并且回收需要主动调用 freeMemory 方法 - ByteBuffer 的实现类内部,使用了
Cleaner(虚引用)来监测 ByteBuffer 对象,一旦 ByteBuffer 对象被垃圾回收,那么就会由ReferenceHandler线程通过Cleaner的clean方法调 用freeMemory来释放直接内存
演示垃圾回收
- 使用
bytebuffer -XX:+DisableExplicitGC 禁用显式的垃圾回收 System.gc();
1 | /** |
- 按下第一次回车出现java进程 占用1GB
- 再次按下回车释放内存
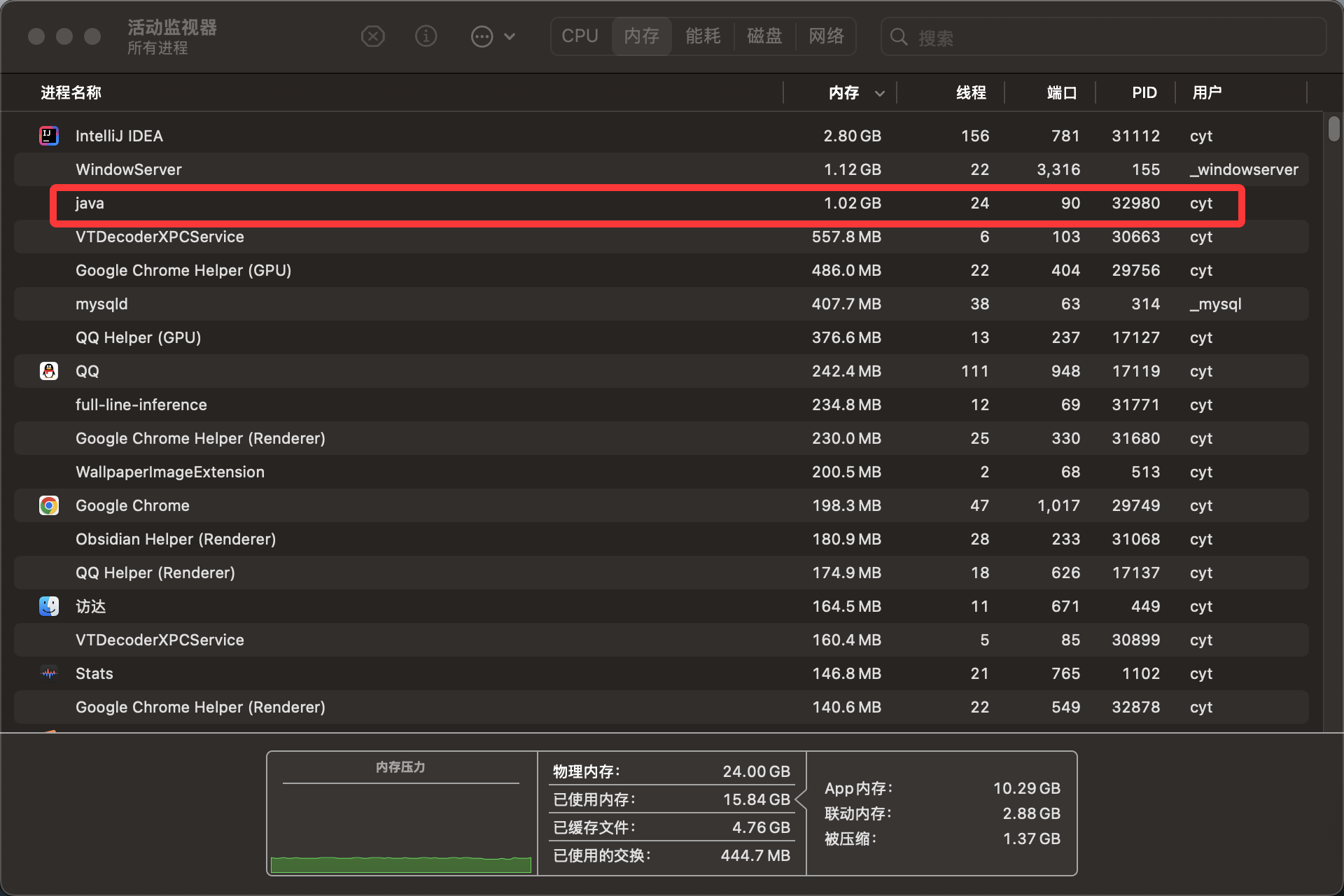
unsafe
- 通过反射获取unsafe
- java不推荐程序员使用
1 | /** |
byteBuffer源码剖析
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(_1Gb);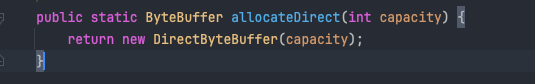
- 多开一个线程
1 | DirectByteBuffer(int cap) { // package-private |
cleaner对象
1 | public class Cleaner |